Mechanisms of toxicity in C9FTLD/ALS
- PMID: 24394885
- PMCID: PMC4002260
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-013-1237-z
Mechanisms of toxicity in C9FTLD/ALS
Abstract
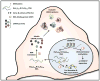
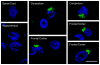
A hexanucleotide repeat expansion within a non-coding region of the C9ORF72 gene is the most common mutation causative of frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Elucidating how this bidirectionally transcribed G4C2·C4G2 expanded repeat causes "C9FTLD/ALS" has since become an important goal of the field. Likely pathogenic mechanisms include toxicity induced by repeat-containing RNAs, and loss of C9orf72 function due to epigenetic changes resulting in decreased C9ORF72 mRNA expression. With regards to the former, sense and antisense transcripts of the expanded repeat aberrantly interact with various RNA-binding proteins and form discrete nuclear structures, termed RNA foci. These foci have the capacity to sequester select RNA-binding proteins, thereby impairing their function. (G4C2)exp and (C4G2)exp transcripts also succumb to an alternative fate: repeat-associated non-ATG (RAN) translation. This unconventional mode of translation, which occurs in the absence of an initiating codon, results in the abnormal production of poly(GA), poly(GP), poly(GR), poly(PR) and poly(PA) peptides, collectively referred to as C9RAN proteins. C9RAN proteins form neuronal inclusions throughout the central nervous system of C9FTLD/ALS patients and may contribute to disease pathogenesis. This review aims to summarize the important findings from studies examining mechanisms of disease in C9FTLD/ALS, and will also highlight some of the many questions in need of further investigation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antisense transcripts of the expanded C9ORF72 hexanucleotide repeat form nuclear RNA foci and undergo repeat-associated non-ATG translation in c9FTD/ALS.Acta Neuropathol. 2013 Dec;126(6):829-44. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1192-8. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Acta Neuropathol. 2013. PMID: 24129584 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional nucleolar dysfunction in C9orf72 frontotemporal lobar degeneration.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2017 Apr 18;5(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s40478-017-0432-x. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2017. PMID: 28420437 Free PMC article.
-
Drosha inclusions are new components of dipeptide-repeat protein aggregates in FTLD-TDP and ALS C9orf72 expansion cases.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2015 Apr;74(4):380-7. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0000000000000182. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25756586 Free PMC article.
-
Unconventional features of C9ORF72 expanded repeat in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal lobar degeneration.Neurobiol Aging. 2014 Oct;35(10):2421.e1-2421.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.04.015. Epub 2014 Apr 19. Neurobiol Aging. 2014. PMID: 24836899 Review.
-
C9orf72 isoforms in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration.Brain Res. 2016 Sep 15;1647:43-49. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.04.062. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27134035 Review.
Cited by
-
Where and Why Modeling Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 12;22(8):3977. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083977. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33921446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling simple repeat expansion diseases with iPSC technology.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Nov;73(21):4085-100. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2284-0. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27261369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenic determinants and mechanisms of ALS/FTD linked to hexanucleotide repeat expansions in the C9orf72 gene.Neurosci Lett. 2017 Jan 1;636:16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.09.007. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Neurosci Lett. 2017. PMID: 27619540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondria Dysfunction in Frontotemporal Dementia/Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Lessons From Drosophila Models.Front Neurosci. 2021 Nov 24;15:786076. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.786076. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34899176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of RNA Metabolism in Neurological Diseases and Emerging Therapeutic Interventions.Neuron. 2019 Apr 17;102(2):294-320. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.03.014. Neuron. 2019. PMID: 30998900 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Mahdawi S, Pinto RM, Ismail O, Varshney D, Lymperi S, Sandi C, Trabzuni D, Pook M. The Friedreich ataxia GAA repeat expansion mutation induces comparable epigenetic changes in human and transgenic mouse brain and heart tissues. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17 (5):735–746. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm346. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Sarraj S, King A, Troakes C, Smith B, Maekawa S, Bodi I, Rogelj B, Al-Chalabi A, Hortobagyi T, Shaw CE. p62 positive, TDP-43 negative, neuronal cytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusions in the cerebellum and hippocampus define the pathology of C9orf72-linked FTLD and MND/ALS. Acta Neuropathol. 2011;122 (6):691–702. doi: 10.1007/s00401-011-0911-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Almeida S, Gascon E, Tran H, Chou HJ, Gendron TF, Degroot S, Tapper AR, Sellier C, Charlet-Berguerand N, Karydas A, Seeley WW, Boxer AL, Petrucelli L, Miller BL, Gao FB. Modeling key pathological features of frontotemporal dementia with C9ORF72 repeat expansion in iPSC-derived human neurons. Acta Neuropathol. 2013;126 (3):385–399. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1149-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ash PE, Bieniek KF, Gendron TF, Caulfield T, Lin WL, Dejesus-Hernandez M, van Blitterswijk MM, Jansen-West K, Paul JW, 3rd, Rademakers R, Boylan KB, Dickson DW, Petrucelli L. Unconventional translation of C9ORF72 GGGGCC expansion generates insoluble polypeptides specific to c9FTD/ALS. Neuron. 2013;77 (4):639–646. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.02.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

