Decorin differentially modulates the activity of insulin receptor isoform A ligands
- PMID: 24389353
- PMCID: PMC4039619
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.12.010
Decorin differentially modulates the activity of insulin receptor isoform A ligands
Abstract
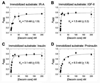
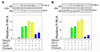
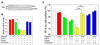
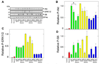
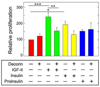
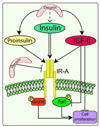
The proteoglycan decorin, a key component of the tumor stroma, regulates the action of several tyrosine-kinase receptors, including the EGFR, Met and the IGF-IR. Notably, the action of decorin in regulating the IGF-I system differs between normal and transformed cells. In normal cells, decorin binds with high affinity to both the natural ligand IGF-I and the IGF-I receptor (IGF-IR) and positively regulates IGF-IR activation and downstream signaling. In contrast, in transformed cells, decorin negatively regulates ligand-induced IGF-IR activation, downstream signaling and IGF-IR-dependent biological responses. Whether decorin may bind another member of the IGF-I system, the insulin receptor A isoform (IR-A) and its cognate ligands, insulin, IGF-II and proinsulin, have not been established. Here we show that decorin bound with high affinity insulin and IGF-II and, to a lesser extent, proinsulin and IR-A. We utilized as a cell model system mouse embryonic fibroblasts homozygous for a targeted disruption of the Igf1r gene (designated R(-) cells) which were stably transfected with a human construct harboring the IR-A isoform of the receptor. Using these R(-)/IR-A cells, we demonstrate that decorin did not affect ligand-induced phosphorylation of the IR-A but enhanced IR-A downregulation after prolonged IGF-II stimulation without affecting insulin and proinsulin-dependent effects on IR-A stability. In addition, decorin significantly inhibited IGF-II-mediated activation of the Akt pathways, without affecting insulin and proinsulin-dependent signaling. Notably, decorin significantly inhibited IGF-II-mediated cell proliferation of R(-)/IR-A cells but affected neither insulin- nor proinsulin-dependent mitogenesis. Collectively, these results suggest that decorin differentially regulates the action of IR-A ligands. Decorin preferentially inhibits IGF-II-mediated biological responses but does not affect insulin- or proinsulin-dependent signaling. Thus, decorin loss may contribute to tumor initiation and progression in malignant neoplasms which depend on an IGF-II/IR-A autocrine loop.
Keywords: Decorin; IR-A; Proliferation; Signaling.
Copyright © 2013 International Society of Matrix Biology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decorin antagonizes IGF receptor I (IGF-IR) function by interfering with IGF-IR activity and attenuating downstream signaling.J Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 7;286(40):34712-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.262766. Epub 2011 Aug 12. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21840990 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin and insulin-like growth factor II differentially regulate endocytic sorting and stability of insulin receptor isoform A.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 30;287(14):11422-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.252478. Epub 2012 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22318726 Free PMC article.
-
Proinsulin binds with high affinity the insulin receptor isoform A and predominantly activates the mitogenic pathway.Endocrinology. 2012 May;153(5):2152-63. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1843. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22355074
-
Dichotomy of decorin activity on the insulin-like growth factor-I system.FEBS J. 2013 May;280(10):2138-49. doi: 10.1111/febs.12149. Epub 2013 Feb 15. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23351020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin receptor (IR) and insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF-1R) signaling systems: novel treatment strategies for cancer.Med Oncol. 2014 Jan;31(1):805. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0805-3. Epub 2013 Dec 14. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24338270 Review.
Cited by
-
Obesity, Diabetes, and Cancer: The Role of the Insulin/IGF Axis; Mechanisms and Clinical Implications.Biomolecules. 2022 Apr 20;12(5):612. doi: 10.3390/biom12050612. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35625539 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the key roles of proteoglycans in breast cancer biology and translational medicine.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Apr;1855(2):276-300. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25829250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble biglycan as a biomarker of inflammatory renal diseases.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Sep;54:223-35. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.07.020. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25091702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pivotal role for decorin in angiogenesis.Matrix Biol. 2015 Apr;43:15-26. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2015.01.023. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Matrix Biol. 2015. PMID: 25661523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sortilin regulates progranulin action in castration-resistant prostate cancer cells.Endocrinology. 2015 Jan;156(1):58-70. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1590. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25365768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker J, Liu JP, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell. 1993;75:73–82. - PubMed
-
- Bartella V, De Marco P, Malaguarnera R, Belfiore A, Maggiolini M. New advances on the functional cross-talk between insulin-like growth factor-I and estrogen signaling in cancer. Cell. Signal. 2012;24:1515–1521. - PubMed
-
- Baserga R. The insulin-like growth factor I receptor: a key to tumor growth? Cancer Res. 1995;55:249–252. - PubMed
-
- Baserga R. The contradictions of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Oncogene. 2000;19:5574–5581. - PubMed
-
- Baserga R, Hongo A, Rubini M, Prisco M, Valentinis B. The IGF-I receptor in cell growth, transformation and apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1997;1332:F105–F126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

