Differential expression of Homer1a in the hippocampus and cortex likely plays a role in radiation-induced brain injury
- PMID: 24377717
- PMCID: PMC4118588
- DOI: 10.1667/RR13475.1
Differential expression of Homer1a in the hippocampus and cortex likely plays a role in radiation-induced brain injury
Abstract
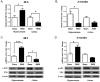
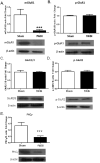
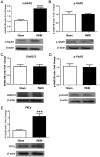
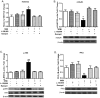
Fractionated partial or whole-brain irradiation is the primary treatment for metastatic brain tumors. Despite reducing tumor burden and increasing lifespan, progressive, irreversible cognitive impairment occurs in >50% of the patients who survive >6 months after fractionated whole-brain irradiation. The exact mechanism(s) responsible for this radiation-induced brain injury are unknown; however, preclinical studies suggest that radiation modulates the extracellular receptor kinase signaling pathway, which is associated with cognitive impairment in many neurological diseases. In the study reported here, we demonstrated that the extracellular receptor kinase transcriptionally-regulated early response gene, Homer1a, was up-regulated transiently in the hippocampus and down-regulated in the cortex of young adult male Fischer 344 X Brown Norway rats at 48 h after 40 Gy of fractionated whole-brain irradiation. Two months after fractionated whole-brain irradiation, these changes in Homer1a expression correlated with a down-regulation of the hippocampal glutamate receptor 1 and protein kinase Cγ, and an up-regulation of cortical glutamate receptor 1 and protein kinase Cγ. Two drugs that prevent radiation-induced cognitive impairment in rats, the angiotensin type-1 receptor blocker, L-158,809, and the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, reversed the fractionated whole-brain irradiation-induced Homer1a expression at 48 h in the hippocampus and cortex and restored glutamate receptor 1 and protein kinase Cγ to the levels in sham-irradiated controls at 2 months after fractionated whole-brain irradiation. These data indicate that Homer1a is, (1) a brain region specific regulator of radiation-induced brain injury, including cognitive impairment and (2) potentially a druggable target for preventing it.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic administration of the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, prevents fractionated whole-brain irradiation-induced perirhinal cortex-dependent cognitive impairment.Radiat Res. 2012 Jul;178(1):46-56. doi: 10.1667/rr2731.1. Epub 2012 Jun 12. Radiat Res. 2012. PMID: 22687052 Free PMC article.
-
Aging masks detection of radiation-induced brain injury.Brain Res. 2011 Apr 18;1385:307-16. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.02.034. Epub 2011 Feb 19. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21338580 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial learning and memory deficits after whole-brain irradiation are associated with changes in NMDA receptor subunits in the hippocampus.Radiat Res. 2006 Dec;166(6):892-9. doi: 10.1667/RR0588.1. Radiat Res. 2006. PMID: 17149974
-
Molecular, Cellular and Functional Effects of Radiation-Induced Brain Injury: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 24;16(11):27796-815. doi: 10.3390/ijms161126068. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26610477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling pathways regulating Homer1a expression: implications for antidepressant therapy.Biol Chem. 2016 Mar;397(3):207-14. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2015-0267. Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26641965 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain diffusion MRI biomarkers after oncology treatments.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2024 Feb 16;28(6):823-834. doi: 10.5603/rpor.98728. eCollection 2023. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2024. PMID: 38515826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole-brain irradiation differentially modifies neurotransmitters levels and receptors in the hypothalamus and the prefrontal cortex.Radiat Oncol. 2020 Nov 23;15(1):269. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-01716-y. Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33228731 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Reorganization Response in the Cochlear Nucleus Following Intense Noise Exposure.Neuroscience. 2019 Feb 10;399:184-198. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.12.023. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 30593923 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation-induced brain injury: current concepts and therapeutic strategies targeting neuroinflammation.Neurooncol Adv. 2020 May 5;2(1):vdaa057. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdaa057. eCollection 2020 Jan-Dec. Neurooncol Adv. 2020. PMID: 32642709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of breathing 100% oxygen on radiation-induced cognitive impairment.Radiat Res. 2014 Nov;182(5):580-5. doi: 10.1667/RR13643.1. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Radiat Res. 2014. PMID: 25338095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2012. Cancer J Clinicians. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global Cancer Statistics. 2011;61:69. - PubMed
-
- Hwang SY, Jung JS, Kim TH, Lim SJ, Oh ES, Kim JY, et al. Ionizing radiation induces astrocyte gliosis through microglia activation. Neurobiol Disease. 2006;21:457–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

