Evaluation of STAT3 signaling in ALDH+ and ALDH+/CD44+/CD24- subpopulations of breast cancer cells
- PMID: 24376586
- PMCID: PMC3871589
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082821
Evaluation of STAT3 signaling in ALDH+ and ALDH+/CD44+/CD24- subpopulations of breast cancer cells
Abstract
Background: STAT3 activation is frequently detected in breast cancer and this pathway has emerged as an attractive molecular target for cancer treatment. Recent experimental evidence suggests ALDH-positive (ALDH(+)), or cell surface molecule CD44-positive (CD44(+)) but CD24-negative (CD24(-)) breast cancer cells have cancer stem cell properties. However, the role of STAT3 signaling in ALDH(+) and ALDH(+)/CD44(+)/CD24(-) subpopulations of breast cancer cells is unknown.
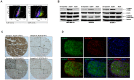
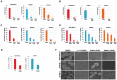
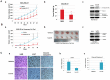
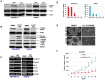
Methods and results: We examined STAT3 activation in ALDH(+) and ALDH(+)/CD44(+)/CD24(-) subpopulations of breast cancer cells by sorting with flow cytometer. We observed ALDH-positive (ALDH(+)) cells expressed higher levels of phosphorylated STAT3 compared to ALDH-negative (ALDH(-)) cells. There was a significant correlation between the nuclear staining of phosphorylated STAT3 and the expression of ALDH1 in breast cancer tissues. These results suggest that STAT3 is activated in ALDH(+) subpopulations of breast cancer cells. STAT3 inhibitors Stattic and LLL12 inhibited STAT3 phosphorylation, reduced the ALDH(+) subpopulation, inhibited breast cancer stem-like cell viability, and retarded tumorisphere-forming capacity in vitro. Similar inhibition of STAT3 phosphorylation, and breast cancer stem cell viability were observed using STAT3 ShRNA. In addition, LLL12 inhibited STAT3 downstream target gene expression and induced apoptosis in ALDH(+) subpopulations of breast cancer cells. Furthermore, LLL12 inhibited STAT3 phosphorylation and tumor cell proliferation, induced apoptosis, and suppressed tumor growth in xenograft and mammary fat pad mouse models from ALDH(+) breast cancer cells. Similar in vitro and tumor growth in vivo results were obtained when ALDH(+) cells were further selected for the stem cell markers CD44(+) and CD24(-).
Conclusion: These studies demonstrate an important role for STAT3 signaling in ALDH(+) and ALDH(+)/CD44(+)/CD24(-) subpopulations of breast cancer cells which may have cancer stem cell properties and suggest that pharmacologic inhibition of STAT3 represents an effective strategy to selectively target the cancer stem cell-like subpopulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
STAT3 as a potential therapeutic target in ALDH+ and CD44+/CD24+ stem cell-like pancreatic cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2016 Dec;49(6):2265-2274. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3728. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27748818 Free PMC article.
-
STAT3 is necessary for proliferation and survival in colon cancer-initiating cells.Cancer Res. 2011 Dec 1;71(23):7226-37. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4660. Epub 2011 Sep 7. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21900397 Free PMC article.
-
ALDH activity selectively defines an enhanced tumor-initiating cell population relative to CD133 expression in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20636. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020636. Epub 2011 Jun 13. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21695188 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer stem cells and intrinsic subtypes: controversies rage on.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009 Jan;4(1):50-60. doi: 10.2174/157488809787169110. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19149630 Review.
-
Breast cancer stem cells: A fallow research ground in Africa.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Oct;216(10):153118. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.153118. Epub 2020 Jul 12. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32853953 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Targeting STAT3 signaling using stabilised sulforaphane (SFX-01) inhibits endocrine resistant stem-like cells in ER-positive breast cancer.Oncogene. 2020 Jun;39(25):4896-4908. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1335-z. Epub 2020 May 30. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 32472077 Free PMC article.
-
HER2 in stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity of breast cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2019 May;21(5):539-555. doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-1961-x. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30306401 Review.
-
FGFR signaling regulates resistance of head and neck cancer stem cells to cisplatin.Oncotarget. 2018 May 18;9(38):25148-25165. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25358. eCollection 2018 May 18. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29861860 Free PMC article.
-
The circRNA circIFI30 promotes progression of triple-negative breast cancer and correlates with prognosis.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jun 4;12(11):10983-11003. doi: 10.18632/aging.103311. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32497020 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Roles of STAT3 Signaling in the Progression of Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2014 Apr 9;6(2):829-59. doi: 10.3390/cancers6020829. Cancers (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24722453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Molofsky A, Pardal R, Morrison S (2004) Diverse mechanisms regulate stem cell self-renewal. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16: 700–707. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

