Phenol-soluble modulins--critical determinants of staphylococcal virulence
- PMID: 24372362
- PMCID: PMC4072763
- DOI: 10.1111/1574-6976.12057
Phenol-soluble modulins--critical determinants of staphylococcal virulence
Abstract
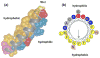
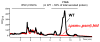
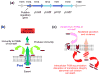
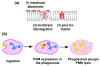
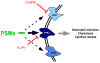
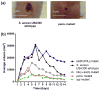
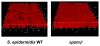
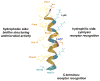
Phenol-soluble modulins (PSMs) are a recently discovered family of amphipathic, alpha-helical peptides that have multiple roles in staphylococcal pathogenesis and contribute to a large extent to the pathogenic success of virulent staphylococci, such as Staphylococcus aureus. PSMs may cause lysis of many human cell types including leukocytes and erythrocytes, stimulate inflammatory responses, and contribute to biofilm development. PSMs appear to have an original role in the commensal lifestyle of staphylococci, where they facilitate growth and spreading on epithelial surfaces. Aggressive, cytolytic PSMs seem to have evolved from that original role and are mainly expressed in highly virulent S. aureus. Here, we will review the biochemistry, genetics, and role of PSMs in the commensal and pathogenic lifestyles of staphylococci, discuss how diversification of PSMs defines the aggressiveness of staphylococcal species, and evaluate potential avenues to target PSMs for drug development against staphylococcal infections.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; Staphylococcus epidermidis; biofilm; phenol-soluble modulin; toxin; virulence.
Published 2014. This article is a US Goverment work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Phenol-soluble modulins.Int J Med Microbiol. 2014 Mar;304(2):164-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.11.019. Epub 2013 Dec 1. Int J Med Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24447915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenol-soluble modulins and staphylococcal infection.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013 Oct;11(10):667-73. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3110. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24018382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenol-Soluble Modulin Toxins of Staphylococcus haemolyticus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 May 24;7:206. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00206. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28596942 Free PMC article.
-
Direct and synergistic hemolysis caused by Staphylococcus phenol-soluble modulins: implications for diagnosis and pathogenesis.Microbes Infect. 2012 Apr;14(4):380-6. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2011.11.013. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Microbes Infect. 2012. PMID: 22178792 Free PMC article.
-
Phenol-soluble modulins: novel virulence-associated peptides of staphylococci.Future Microbiol. 2014;9(2):203-16. doi: 10.2217/fmb.13.153. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Future Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24295365 Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular persistence of Staphylococcus aureus in endothelial cells is promoted by the absence of phenol-soluble modulins.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):1186-1198. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1910455. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 33843450 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin Resistance Elements in the Canine Pathogen Staphylococcus pseudintermedius and Their Association with the Peptide Toxin PSM-mec.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jan 28;13(2):130. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13020130. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38391516 Free PMC article.
-
A clash of quorum sensing vs quorum sensing inhibitors: an overview and risk of resistance.Arch Microbiol. 2023 Mar 7;205(4):107. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03442-x. Arch Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36881156 Review.
-
Host-Specific Evolutionary and Transmission Dynamics Shape the Functional Diversification of Staphylococcus epidermidis in Human Skin.Cell. 2020 Feb 6;180(3):454-470.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.01.006. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32004459 Free PMC article.
-
The Small RNA Teg41 Regulates Expression of the Alpha Phenol-Soluble Modulins and Is Required for Virulence in Staphylococcus aureus.mBio. 2019 Feb 5;10(1):e02484-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02484-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30723124 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adhikari RP, Ajao AO, Aman MJ, Karauzum H, Sarwar J, Lydecker AD, Johnson JK, Nguyen C, Chen WH, Roghmann MC. Lower antibody levels to Staphylococcus aureus exotoxins are associated with sepsis in hospitalized adults with invasive S. aureus infections. J Infect Dis. 2012;206:915–923. - PubMed
-
- Adkins I, Holubova J, Kosova M, Sadilkova L. Bacteria and their toxins tamed for immunotherapy. Curr Pharm Biotech. 2012;13:1446–1473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

