Antigen-specific gene therapy after immunisation reduces the severity of collagen-induced arthritis
- PMID: 24371448
- PMCID: PMC3858880
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/345092
Antigen-specific gene therapy after immunisation reduces the severity of collagen-induced arthritis
Abstract
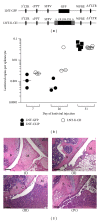
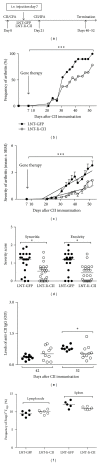
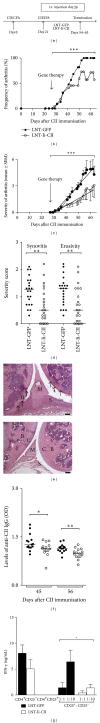
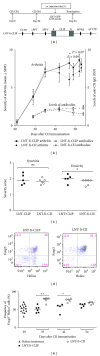
Reestablishment of tolerance induction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) would be an optimal treatment with few, if any, side effects. However, to develop such a treatment further insights in the immunological mechanisms governing tolerance are needed. We have developed a model of antigen-specific tolerance in collagen type II (CII) induced arthritis (CIA) using lentivirus-based gene therapy. The immunodominant epitope of CII was inserted into a lentivirus vector to achieve expression on the MHC class II molecule and the lentiviral particles were subsequently intravenously injected at different time points during CIA. Injection of lentiviral particles in early phases of CIA, that is, at day 7 or day 26 after CII immunisation, partially prevented development of arthritis, decreased the serum levels of CII-specific IgG antibodies, and enhanced the suppressive function of CII-specific T regulatory cells. When lentiviral particles were injected during manifest arthritis, that is, at day 31 after CII immunisation, the severity of arthritis progression was ameliorated, the levels of CII-specific IgG antibodies decreased and the proportion of T regulatory cells increased. Thus, antigen-specific gene therapy is effective when administered throughout the inflammatory course of arthritis and offers a good model for investigation of the basic mechanisms during tolerance in CIA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tolerance induction using lentiviral gene delivery delays onset and severity of collagen II arthritis.Mol Ther. 2009 Apr;17(4):632-40. doi: 10.1038/mt.2009.299. Epub 2009 Jan 27. Mol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19174762 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of collagen type II-specific immune responses during development of collagen-induced arthritis in two B10 mouse strains.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 Nov 1;14(6):R237. doi: 10.1186/ar4080. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 23116329 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination with a Novel Antigen-Specific Tolerizing DNA Vaccine Encoding CCOL2A1 Protects Rats from Experimental Rheumatoid Arthritis.Hum Gene Ther. 2019 Jan;30(1):69-78. doi: 10.1089/hum.2018.042. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Hum Gene Ther. 2019. PMID: 29901407
-
Type II collagen oral tolerance; mechanism and role in collagen-induced arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.Mod Rheumatol. 2009;19(6):581-9. doi: 10.1007/s10165-009-0210-0. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Mod Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19697097 Review.
-
Role of glycopeptide-specific T cells in collagen-induced arthritis: an example how post-translational modification of proteins may be involved in autoimmune disease.Ann Med. 2001 Oct;33(7):456-65. doi: 10.3109/07853890109002094. Ann Med. 2001. PMID: 11680793 Review.
Cited by
-
Autoimmune Aspects of Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Diseases: A Template for Innovative Therapy.Front Psychiatry. 2017 Apr 4;8:46. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00046. eCollection 2017. Front Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28421005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Commercial bovine proteoglycan is highly arthritogenic and can be used as an alternative antigen source for PGIA model.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:148594. doi: 10.1155/2014/148594. Epub 2014 May 27. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24971313 Free PMC article.
-
Lentiviral-Mediated Systemic RNA Interference In Vivo.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2766:153-161. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3682-4_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38270875
-
(5R)-5-hydroxytriptolide (LLDT-8) prevents collagen-induced arthritis through OPG/RANK/RANKL signaling in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Nov;12(5):3101-3106. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3739. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27882124 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Therapy for Autoimmune Disease.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015 Oct;49(2):163-76. doi: 10.1007/s12016-014-8451-x. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25277817 Review.
References
-
- Isaacs JD. Therapeutic agents for patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor-α antagonists. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. 2009;9(12):1463–1475. - PubMed
-
- Scheinecker C, Redlich K, Smolen JS. Cytokines as therapeutic targets: advances and limitations. Immunity. 2008;28(4):440–444. - PubMed
-
- Rosloniec EF, Whittington KB, Zaller DM, Kang AH. HLA-DR1 (DRB1*0101) and DR4 (DRB1*0401) use the same anchor residues for binding an immunodominant peptide derived from human type II collagen. Journal of Immunology. 2002;168(1):253–259. - PubMed
-
- Andersson EC, Hansen BE, Jacobsen H, et al. Definition of MHC and T cell receptor contacts in the HLA-DR4-restricted immunodominant epitope in type II collagen and characterization of collagen-induced arthritis in HLA-DR4 and human CD4 transgenic mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1998;95(13):7574–7579. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

