Oxidative stress and antioxidant activity in hypothermia and rewarming: can RONS modulate the beneficial effects of therapeutic hypothermia?
- PMID: 24363826
- PMCID: PMC3865646
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/957054
Oxidative stress and antioxidant activity in hypothermia and rewarming: can RONS modulate the beneficial effects of therapeutic hypothermia?
Abstract
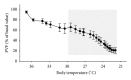
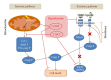
Hypothermia is a condition in which core temperature drops below the level necessary to maintain bodily functions. The decrease in temperature may disrupt some physiological systems of the body, including alterations in microcirculation and reduction of oxygen supply to tissues. The lack of oxygen can induce the generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen free radicals (RONS), followed by oxidative stress, and finally, apoptosis and/or necrosis. Furthermore, since the hypothermia is inevitably followed by a rewarming process, we should also consider its effects. Despite hypothermia and rewarming inducing injury, many benefits of hypothermia have been demonstrated when used to preserve brain, cardiac, hepatic, and intestinal function against ischemic injury. This review gives an overview of the effects of hypothermia and rewarming on the oxidant/antioxidant balance and provides hypothesis for the role of reactive oxygen species in therapeutic hypothermia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of superoxide ion formation in hypothermia/rewarming induced contractile dysfunction in cardiomyocytes.Cryobiology. 2018 Apr;81:57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2018.02.010. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Cryobiology. 2018. PMID: 29458041 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate hypothermia protects against systemic oxidative stress in a rat model of intestinal ischemia and reperfusion injury.Shock. 2005 Aug;24(2):159-64. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000168871.60531.6f. Shock. 2005. PMID: 16044087
-
Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species-Induced Protein Modifications: Implication in Carcinogenesis and Anticancer Therapy.Cancer Res. 2018 Nov 1;78(21):6040-6047. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0980. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30327380 Review.
-
Hypothermia-rewarming: A Double-edged sword?Med Hypotheses. 2019 Dec;133:109387. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2019.109387. Epub 2019 Aug 30. Med Hypotheses. 2019. PMID: 31541781
-
The impact of environmental contamination on the generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species - Consequences for plants and humans.Environ Int. 2018 Oct;119:133-151. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.06.019. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Environ Int. 2018. PMID: 29957355 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia-Ischemia and Hypothermia Independently and Interactively Affect Neuronal Pathology in Neonatal Piglets with Short-Term Recovery.Dev Neurosci. 2019;41(1-2):17-33. doi: 10.1159/000496602. Epub 2019 May 20. Dev Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31108487 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Vascular Impairment, Neuroinflammation, and Oxidative Stress Dynamics with Whole-Body Cryotherapy in Multiple Sclerosis Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 29;25(7):3858. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073858. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mild Hypothermia Promotes Ischemic Tolerance and Survival of Neural Stem Cell Grafts by Enhancing Global SUMOylation.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 May 27;2022:6503504. doi: 10.1155/2022/6503504. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Dec 29;2023:9894206. doi: 10.1155/2023/9894206. PMID: 35669854 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Effect of temperature on FAD and NADH-derived signals and neurometabolic coupling in the mouse auditory and motor cortex.Pflugers Arch. 2017 Dec;469(12):1631-1649. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-2037-4. Epub 2017 Aug 7. Pflugers Arch. 2017. PMID: 28785802 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Profile in a Preclinical Kidney Transplantation Model According to Different Preservation Modalities.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 5;24(2):1029. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021029. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674540 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanania NA, Zimmerman JL. Accidental hypothermia. Critical Care Clinics. 1999;15(2):235–249. - PubMed
-
- Nedergaard J, Bengtsson T, Cannon B. Unexpected evidence for active brown adipose tissue in adult humans. The American Journal of Physiology—Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2007;293(2):E444–E452. - PubMed
-
- Nedergaard J, Cannon B. The changed metabolic world with human brown adipose tissue: therapeutic visions. Cell Metabolism. 2010;11(4):268–272. - PubMed
-
- Van Marken Lichtenbelt WD, Vanhommerig JW, Smulders NM, et al. Cold-activated brown adipose tissue in healthy men. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2009;360(15):1500–1508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

