High transcript levels of vitamin D receptor are correlated with higher mRNA expression of human beta defensins and IL-10 in mucosa of HIV-1-exposed seronegative individuals
- PMID: 24349345
- PMCID: PMC3857805
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082717
High transcript levels of vitamin D receptor are correlated with higher mRNA expression of human beta defensins and IL-10 in mucosa of HIV-1-exposed seronegative individuals
Abstract
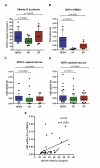
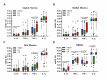
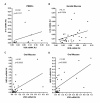
Vitamin D (VitD) is an endogenous immunomodulator that could protect from HIV-1 infection reducing immune activation and inducing the expression of anti-HIV-1 peptides. To establish a correlation between VitD and natural resistance to HIV-1 infection, a case-control study using blood and mucosa samples of 58 HIV-1-exposed but seronegative (HESN) individuals, 43 HIV-1 seropositives (SPs) and 59 non-exposed healthy controls (HCs) was carried out. The VitD concentration in plasma was determined by ELISA, and mRNA relative units (RU) of VDR, IL-10, TGF-β, TNF-α and IL-1β in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), oral and genital mucosa was quantified by qRT-PCR. mRNA levels of human beta-defensin (HBD) -2 and -3 were previously reported and used for correlations. Significantly higher levels of VitD were found in plasma as well as higher mRNA RU of VDR in PBMCs, and in genital mucosa from HESN compared to HCs. In addition, higher mRNA RU of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-10, and lower mRNA RU of TGF-β were found in PBMC from HESNs compared to HCs. We also observed higher IL-10 mRNA RU in genital mucosa of HESNs compared to HCs, and the mRNA levels of TNF-α in oral and genital mucosa of SPs were higher compared to HESNs. Furthermore, positive correlations between VDR and IL-10 mRNA RU in PBMCs and genital mucosa of HESNs were found. Finally, HBD-2 and HBD-3 mRNA RU were positively correlated with VDR mRNA expression in oral mucosa from HESNs. These results suggest that high levels of VitD and its receptor are associated with natural resistance to HIV-1 infection. Up-regulation of the anti-inflammatory IL-10, and the induction of anti-HIV-1 defensins in mucosa might be part of the mechanisms involved in this association. However, further studies are required to define causal associations.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic associations of the vitamin D and antiviral pathways with natural resistance to HIV-1 infection are influenced by interpopulation variability.Infect Genet Evol. 2019 Sep;73:276-286. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.05.014. Epub 2019 May 16. Infect Genet Evol. 2019. PMID: 31103723
-
High Expression of Antiviral and Vitamin D Pathway Genes Are a Natural Characteristic of a Small Cohort of HIV-1-Exposed Seronegative Individuals.Front Immunol. 2017 Feb 13;8:136. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00136. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28243241 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral molecules correlate with vitamin D pathway genes and are associated with natural resistance to HIV-1 infection.Microbes Infect. 2016 Jul-Aug;18(7-8):510-6. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2016.03.015. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Microbes Infect. 2016. PMID: 27083474
-
Vitamin D in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection: Influence on Immunity and Disease.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 12;9:458. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00458. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29593721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for the innate immune response as a correlate of protection in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 highly exposed seronegative subjects (HESN).Clin Exp Immunol. 2011 May;164(2):158-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04379.x. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21413945 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Interplay Between Cervicovaginal Microbial Dysbiosis and Cervicovaginal Immunity.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 10;13:857299. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.857299. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35359942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ramping Up Antimicrobial Peptides Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Jun 21;8:620806. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.620806. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34235176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Advantages of a Well-balanced Nutrition Regimen for People Living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type -1.J AIDS HIV Treat. 2024;6(1):11-27. doi: 10.33696/aids.6.048. J AIDS HIV Treat. 2024. PMID: 38845818 Free PMC article.
-
Transient Increases in Inflammation and Proapoptotic Potential Are Associated with the HESN Phenotype Observed in a Subgroup of Kenyan Female Sex Workers.Viruses. 2022 Feb 25;14(3):471. doi: 10.3390/v14030471. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35336878 Free PMC article.
-
Human Beta-Defensin 2 and 3 Inhibit HIV-1 Replication in Macrophages.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Jul 1;11:535352. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.535352. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34277460 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

