Circulating C19MC microRNAs in preeclampsia, gestational hypertension, and fetal growth restriction
- PMID: 24347821
- PMCID: PMC3848305
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/186041
Circulating C19MC microRNAs in preeclampsia, gestational hypertension, and fetal growth restriction
Abstract
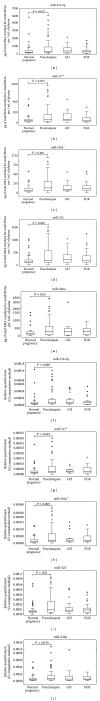
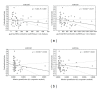
The objective of the study was to identify the profile of circulating C19MC microRNAs (miR-516-5p, miR-517*, miR-518b, miR-520a*, miR-520h, miR-525, and miR-526a) in patients with established preeclampsia (n = 63), fetal growth restriction (n = 27), and gestational hypertension (n = 23). We examined the correlation between plasmatic concentrations and expression levels of microRNAs and the severity of the disease with respect to clinical signs, requirements for the delivery, and Doppler ultrasound parameters. Using absolute and relative quantification approaches, increased extracellular C19MC microRNA levels (miR-516-5p, P = 0.037, P = 0.009; miR-517*, P = 0.033, P = 0.043; miR-520a*, P = 0.001, P = 0.009; miR-525, P = 0.026, P = 0.01; miR-526a, P = 0.03, P = 0.035) were detected in patients with preeclampsia. The association analysis pointed to no relationship between C19MC microRNA plasmatic concentrations and expression profile and identified risk factors for a poorer perinatal outcome. However, the dependence between the levels of plasmatic C19MC microRNAs and the pulsatility index in the middle cerebral artery and the values of cerebroplacental ratio was demonstrated. The study brought the interesting finding that the upregulation of miR-516-5p, miR-517*, miR-520a*, miR-525, and miR-526a is a characteristic phenomenon of established preeclampsia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Prediction of Gestational Hypertension, Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction via the First Trimester Screening of Plasma Exosomal C19MC microRNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 18;20(12):2972. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122972. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31216670 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profile of C19MC microRNAs in placental tissue in pregnancy-related complications.DNA Cell Biol. 2015 Jun;34(6):437-57. doi: 10.1089/dna.2014.2687. Epub 2015 Mar 31. DNA Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25825993 Free PMC article.
-
First trimester screening of circulating C19MC microRNAs can predict subsequent onset of gestational hypertension.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 15;9(12):e113735. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113735. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25502889 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Cluster C19MC in Pre-Eclampsia Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13836. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213836. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Modern methods of early screening for preeclampsia and pregnancy-induced hypertension--a review].Ginekol Pol. 2012 Sep;83(9):688-93. Ginekol Pol. 2012. PMID: 23342898 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Early Detection of Preeclampsia Using Circulating Small non-coding RNA.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 21;8(1):3401. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21604-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29467498 Free PMC article.
-
Sexually dimorphic patterns in maternal circulating microRNAs in pregnancies complicated by fetal growth restriction.Biol Sex Differ. 2021 Nov 17;12(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13293-021-00405-z. Biol Sex Differ. 2021. PMID: 34789323 Free PMC article.
-
The implications of exosomes in pregnancy: emerging as new diagnostic markers and therapeutics targets.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Apr 12;20(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00853-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 35414084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Prediction of Gestational Hypertension, Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction via the First Trimester Screening of Plasma Exosomal C19MC microRNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 18;20(12):2972. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122972. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31216670 Free PMC article.
-
Preeclamptic Women Have Disrupted Placental microRNA Expression at the Time of Preeclampsia Diagnosis: Meta-Analysis.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Dec 24;9:782845. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.782845. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 35004644 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Redman CWG, Sargent IL. Preeclampsia and the systemic inflammatory response. Seminars in Nephrology. 2004;24(6):565–570. - PubMed
-
- Nelson DM. Apoptotic changes occur in syncytiotrophoblast of human placental villi where fibrin type fibrinoid is deposited at discontinuities in the villous trophoblast. Placenta. 1996;17(7):387–391. - PubMed
-
- Oudejans CBM, Tjoa ML, Westerman BA, Mulders MAM, Van Wijk IJ, Van Vugt JMG. Circulating trophoblast in maternal blood. Prenatal Diagnosis. 2003;23(2):111–116. - PubMed
-
- Huppertz B, Kingdom JCP. Apoptosis in the trophoblast—role of apoptosis in placental morphogenesis. Journal of the Society for Gynecologic Investigation. 2004;11(6):353–362. - PubMed
-
- Orozco AF, Bischoff FZ, Horne C, Popek E, Simpson JL, Lewis DE. Hypoxia-induced membrane-bound apoptotic DNA particles: potential mechanism of fetal DNA in maternal plasma. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2006;1075:57–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

