Identification of suppressors of mbk-2/DYRK by whole-genome sequencing
- PMID: 24347622
- PMCID: PMC3931558
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.113.009126
Identification of suppressors of mbk-2/DYRK by whole-genome sequencing
Abstract
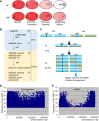
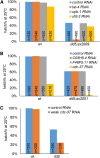
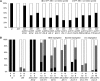
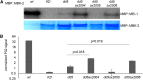
Screening for suppressor mutations is a powerful method to isolate genes that function in a common pathway or process. Because suppressor mutations often do not have phenotypes on their own, cloning of suppressor loci can be challenging. A method combining whole-genome sequencing (WGS) and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mapping (WGS/SNP mapping) was developed to identify mutations with visible phenotypes in C. elegans. We show here that WGS/SNP mapping is an efficient method to map suppressor mutations without the need for previous phenotypic characterization. Using RNA-mediated interference to test candidate loci identified by WGS/SNP mapping, we identified 10 extragenic and six intragenic suppressors of mbk-2, a DYRK family kinase required for the transition from oocyte to zygote. Remarkably, seven suppressors are mutations in cell-cycle regulators that extend the timing of the oocyte-to-zygote transition.
Keywords: C. elegans; DYRK kinase; MBK-2; single nucleotide polymorphism mapping; suppressors; whole-genome sequencing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of MBK-2/Dyrk kinase by dynamic cortical anchoring during the oocyte-to-zygote transition.Curr Biol. 2007 Sep 18;17(18):1545-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.08.049. Curr Biol. 2007. PMID: 17869113
-
Regulation of MBK-2/DYRK by CDK-1 and the pseudophosphatases EGG-4 and EGG-5 during the oocyte-to-embryo transition.Cell. 2009 Oct 30;139(3):560-72. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.08.047. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19879842 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans mutant identification with a one-step whole-genome-sequencing and SNP mapping strategy.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 8;5(11):e15435. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015435. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21079745 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the power of genetics: fast forward genetics in Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Genet Genomics. 2021 Jan;296(1):1-20. doi: 10.1007/s00438-020-01721-6. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Mol Genet Genomics. 2021. PMID: 32888055 Review.
-
A Caenorhabditis elegans genetic-interaction map wiggles into view.J Biol. 2008;7(3):8. doi: 10.1186/jbiol70. Epub 2008 Mar 7. J Biol. 2008. PMID: 18341704 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping Challenging Mutations by Whole-Genome Sequencing.G3 (Bethesda). 2016 May 3;6(5):1297-304. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.028316. G3 (Bethesda). 2016. PMID: 26945029 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of NEKL-4/NEK10 and TTLL genes suppress neuronal ciliary degeneration caused by loss of CCPP-1 deglutamylase function.PLoS Genet. 2020 Oct 16;16(10):e1009052. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009052. eCollection 2020 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 33064774 Free PMC article.
-
The E2F-DP1 Transcription Factor Complex Regulates Centriole Duplication in Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2016 Jan 15;6(3):709-20. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.025577. G3 (Bethesda). 2016. PMID: 26772748 Free PMC article.
-
From phenologs to silent suppressors: Identifying potential therapeutic targets for human disease.Mol Reprod Dev. 2017 Nov;84(11):1118-1132. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22880. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Mol Reprod Dev. 2017. PMID: 28834577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Approaches for Mutation Mapping and Identification in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2016 Oct;204(2):451-474. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.186197. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27729495 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beers M., Kemphues K., 2006. Depletion of the co-chaperone CDC-37 reveals two modes of PAR-6 cortical association in C. elegans embryos. Development 133: 3745–3754 - PubMed
-
- Budirahardja Y., Gonczy P., 2008. PLK-1 asymmetry contributes to asynchronous cell division of C. elegans embryos. Development 135: 1303–1313 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
