Interleukin-6 released by colon cancer-associated fibroblasts is critical for tumour angiogenesis: anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody suppressed angiogenesis and inhibited tumour-stroma interaction
- PMID: 24346288
- PMCID: PMC3899773
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2013.748
Interleukin-6 released by colon cancer-associated fibroblasts is critical for tumour angiogenesis: anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody suppressed angiogenesis and inhibited tumour-stroma interaction
Abstract
Background: Interleukin-6 (IL-6) has an important role in cancer progression, and high levels of plasma IL-6 are correlated with a poor prognosis in a variety of cancers. It has also been reported that tumour stromal fibroblasts are necessary for steps in cancer progression, such as angiogenesis. There have been few reports of a correlation between fibroblast actions and IL-6 levels. In this study, we examined the correlation between cancer stromal fibroblasts and IL-6 and the utility of IL-6 as a therapeutic target in human colon cancer.
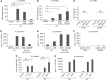
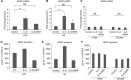
Methods: The expression levels of IL-6 and VEGF of fibroblasts and cancer cell lines were evaluated using real-time PCR and ELISA. The anti-angiogenic effect of inhibiting IL-6 signalling was measured in an angiogenesis model and animal experiment.
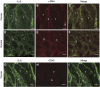
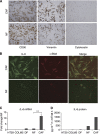
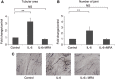
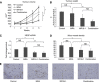
Results: We demonstrate that stromal fibroblasts isolated from colon cancer produced significant amounts of IL-6 and that colon cancer cells enhanced IL-6 production by stromal fibroblasts. Moreover, IL-6 enhanced VEGF production by fibroblasts, thereby inducing angiogenesis. In vivo, anti-IL6 receptor antibody targeting stromal tissue showed greater anti-tumour activity than did anti-IL6 receptor antibody targeting xenografted cancer cells.
Conclusion: Cancer stromal fibroblasts were an important source of IL-6 in colon cancer. IL-6 produced by activated fibroblasts induced tumour angiogenesis by stimulating adjacent stromal fibroblasts. The relationship between IL-6 and stromal fibroblasts offers new approaches to cancer therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-1 Receptor Type 2 Acts with c-Fos to Enhance the Expression of Interleukin-6 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A in Colon Cancer Cells and Induce Angiogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2015 Sep 4;290(36):22212-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.644823. Epub 2015 Jul 24. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26209639 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 mediates epithelial-stromal interactions and promotes gastric tumorigenesis.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 12;8(4):e60914. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060914. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593346 Free PMC article.
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid suppresses angiogenesis via reducing secretion of IL‑6 and VEGF from colon cancer‑associated fibroblasts.Oncol Rep. 2019 Jul;42(1):339-349. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7141. Epub 2019 May 2. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31059084
-
Fibrocytes: A Novel Stromal Cells to Regulate Resistance to Anti-Angiogenic Therapy and Cancer Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 29;19(1):98. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010098. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29286323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting tumor micro-environment for design and development of novel anti-angiogenic agents arresting tumor growth.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013 Nov;113(2):333-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24139944 Review.
Cited by
-
A Potential Role of IL-6/IL-6R in the Development and Management of Colon Cancer.Membranes (Basel). 2021 Apr 24;11(5):312. doi: 10.3390/membranes11050312. Membranes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33923292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic resistance.Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):11553-11572. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5098-7. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27260630 Review.
-
Humanized anti-hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) antibody suppresses innate irinotecan (CPT-11) resistance induced by fibroblast-derived HGF.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 15;6(27):24047-60. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4369. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26090722 Free PMC article.
-
Intimate communications within the tumor microenvironment: stromal factors function as an orchestra.J Biomed Sci. 2023 Jan 4;30(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00894-z. J Biomed Sci. 2023. PMID: 36600243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding RNAs in inflammation and colorectal cancer.RNA Biol. 2020 Nov;17(11):1628-1635. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1705610. Epub 2019 Dec 26. RNA Biol. 2020. PMID: 31847691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anglesio MS, George J, Kulbe H, Friedlander M, Rischin D, Lemech C, Power J, Coward J, Cowin PA, House CM, Chakravarty P, Gorringe KL, Campbell IG, Australian Ovarian Cancer Study Group. Okamoto A, Birrer MJ, Huntsman DG, de Fazio A, Kalloger SE, Balkwill F, Gilks CB, Bowtell DD. IL6-STAT3-HIF signaling and therapeutic response to the angiogenesis inhibitor sunitinib in ovarian clear cell cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:2538–2548. - PubMed
-
- Bishop E, Bell G, Bloor S, Broom I, Hendry N, Wheathley D. An in vitro model of angiogenesis: basic feature. Angiogenesis. 1999;3:335–344. - PubMed
-
- Coward J, Kulbe H, Chakravarty P, Leader D, Vassileva V, Leinster DA, Thompson R, Schioppa T, Nemeth J, Vermeulen J, Singh N, Avril N, Cummings J, Rexhepaj E, Jirström K, Gallagher WM, Brennan DJ, McNeish IA, Balkwill FR. Interleukin-6 as a therapeutic target in human ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:6083–6096. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

