The role of FAK in tumor metabolism and therapy
- PMID: 24333503
- PMCID: PMC6349254
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.12.003
The role of FAK in tumor metabolism and therapy
Abstract
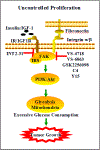
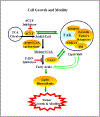
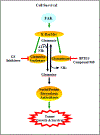
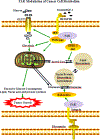
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) plays a vital role in tumor cell proliferation, survival and migration. Altered metabolic pathways fuel rapid tumor growth by accelerating glucose, lipid and glutamine processing. Besides the mitogenic effects of FAK, evidence is accumulating supporting the association between hyper-activated FAK and aberrant metabolism in tumorigenesis. FAK can promote glucose consumption, lipogenesis, and glutamine dependency to promote cancer cell proliferation, motility, and survival. Clinical studies demonstrate that FAK-related alterations of tumor metabolism are associated with increased risk of developing solid tumors. Since FAK contributes to the malignant phenotype, small molecule inhibition of FAK-stimulated bioenergetic and biosynthetic processes can provide a novel approach for therapeutic intervention in tumor growth and invasion.
Keywords: Focal adhesion kinase; Glutamine; Lipogenesis; Molecular targeting; Motility; Proliferation.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Focal adhesion kinase as a cancer therapy target.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2010 Dec;10(10):735-41. doi: 10.2174/187152010794728648. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 21214510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase by PF-562,271 inhibits the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer concomitant with altering the tumor microenvironment.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Nov;10(11):2135-45. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0261. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21903606 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of nuclear focal adhesion kinase (FAK) on Cancer: a focused review.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 11;38(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1265-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31186061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focal adhesion kinase-An emerging viable target in cancer and development of focal adhesion kinase inhibitors.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021 Mar;97(3):774-794. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13808. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021. PMID: 33191630 Review.
-
Targeting FAK in anticancer combination therapies.Nat Rev Cancer. 2021 May;21(5):313-324. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00340-6. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33731845 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of a Polyherbal Mixture in Dairy Calves: Growth Performance and Gene Expression.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Jan 26;7:623710. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.623710. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 33575280 Free PMC article.
-
Phase I Study of BI 853520, an Inhibitor of Focal Adhesion Kinase, in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Nonhematologic Malignancies.Target Oncol. 2019 Feb;14(1):43-55. doi: 10.1007/s11523-018-00617-1. Target Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30756308 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
An EGFR/Src-dependent β4 integrin/FAK complex contributes to malignancy of breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 9;5:16408. doi: 10.1038/srep16408. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26549523 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoarchitecture of Breast Cancer Cells under Diabetic Conditions: Role of Regulatory Kinases-Rho Kinase and Focal Adhesion Kinase.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 15;16(18):3166. doi: 10.3390/cancers16183166. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335137 Free PMC article.
-
SIPA1 boosts migration and proliferation, and blocks apoptosis of glioma by activating the phosphorylation of the FAK signaling pathway.J Med Biochem. 2022 Feb 2;41(1):108-114. doi: 10.5937/jomb0-32903. J Med Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35431649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- (ECCO), T. E. C. O. (2012). Mesothelioma drug slows disease progression in patients with an inactive NF2 gene. In ScienceDaily.
-
- Ackermann M, Morse BA, Delventhal V, Carvajal IM, & Konerding MA (2012). Anti-VEGFR2 and anti-IGF-1R-Adnectins inhibit Ewing’s sarcoma A673-xenograft growth and normalize tumor vascular architecture. Angiogenesis, 15, 685–695. - PubMed
-
- Aleksandrova K, Boeing H, Jenab M, Bas Bueno-de-Mesquita H, Jansen E, van Duijnhoven FJ, Fedirko V, Rinaldi S, Romieu I, Riboli E, Romaguera D, Overvad K, Ostergaard JN, Olsen A, Tjonneland A, Boutron-Ruault MC, Clavel-Chapelon F, Morois S, Masala G, Agnoli C, Panico S, Tumino R, Vineis P, Kaaks R, Lukanova A, Trichopoulou A, Naska A, Bamia C, Peeters PH, Rodriguez L, Buckland G, Sanchez MJ, Dorronsoro M, Huerta JM, Barricarte A, Hallmans G, Palmqvist R, Khaw KT, Wareham N, Allen NE, Tsilidis KK, & Pischon T (2011). Metabolic syndrome and risks of colon and rectal cancer: the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition study. Cancer Prev Res (Phila), 4, 1873–1883. - PubMed
-
- Andersson S, D’Arcy P, Larsson O, & Sehat B (2009). Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activates and stabilizes IGF-1 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 387, 36–41. - PubMed
-
- Anichini E, Zamperini A, Chevanne M, Caldini R, Pucci M, Fibbi G, & Del Rosso M (1997). Interaction of urokinase-type plasminogen activator with its receptor rapidly induces activation of glucose transporters. Biochemistry, 36, 3076–3083. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

