Pathophysiology and treatment of type 2 diabetes: perspectives on the past, present, and future
- PMID: 24315620
- PMCID: PMC4226760
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62154-6
Pathophysiology and treatment of type 2 diabetes: perspectives on the past, present, and future
Abstract
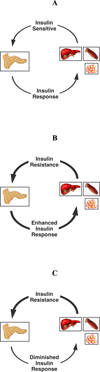
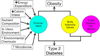
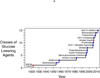
Glucose metabolism is normally regulated by a feedback loop including islet β cells and insulin-sensitive tissues, in which tissue sensitivity to insulin affects magnitude of β-cell response. If insulin resistance is present, β cells maintain normal glucose tolerance by increasing insulin output. Only when β cells cannot release sufficient insulin in the presence of insulin resistance do glucose concentrations rise. Although β-cell dysfunction has a clear genetic component, environmental changes play an essential part. Modern research approaches have helped to establish the important role that hexoses, aminoacids, and fatty acids have in insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction, and the potential role of changes in the microbiome. Several new approaches for treatment have been developed, but more effective therapies to slow progressive loss of β-cell function are needed. Recent findings from clinical trials provide important information about methods to prevent and treat type 2 diabetes and some of the adverse effects of these interventions. However, additional long-term studies of drugs and bariatric surgery are needed to identify new ways to prevent and treat type 2 diabetes and thereby reduce the harmful effects of this disease.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[And what about diabetes?].Bull Acad Natl Med. 2007 Apr-May;191(4-5):941-3; discussion 943. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2007. PMID: 18225448 French.
-
Development and characterization of a novel rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus: the UC Davis type 2 diabetes mellitus UCD-T2DM rat.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008 Dec;295(6):R1782-93. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.90635.2008. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18832086 Free PMC article.
-
A surrogate of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (the enterogastro anastomosis surgery) regulates multiple beta-cell pathways during resolution of diabetes in ob/ob mice.EBioMedicine. 2020 Aug;58:102895. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102895. Epub 2020 Jul 30. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 32739864 Free PMC article.
-
Protection of pancreatic beta-cells: is it feasible?Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2008 Jan;18(1):74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2007.05.004. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2008. PMID: 18096375 Review.
-
Fate of the beta-cell in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes.J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2009 Sep-Oct;49 Suppl 1:S10-5. doi: 10.1331/JAPhA.2009.09076. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2009. PMID: 19801360 Review.
Cited by
-
Combining Nationwide Cohorts to Unveil the Predictive Role of Insulin Resistance and Impaired Insulin Secretion in Diabetes.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2024 Oct;39(5):699-700. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2024.2189. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2024. PMID: 39476815 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Astragalus mongholicus powder, a traditional Chinese medicine formula ameliorate type 2 diabetes by regulating adipoinsular axis in diabetic mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 15;13:973927. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.973927. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36046814 Free PMC article.
-
Amylin at the interface between metabolic and neurodegenerative disorders.Front Neurosci. 2015 Jun 16;9:216. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00216. eCollection 2015. Front Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26136651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated circulating irisin is associated with lower risk of insulin resistance: association and path analyses of obese Chinese adults.BMC Endocr Disord. 2016 Jul 29;16(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12902-016-0123-9. BMC Endocr Disord. 2016. PMID: 27473122 Free PMC article.
-
Vanadium Complexes with Thioanilide Derivatives of Amino Acids: Inhibition of Human Phosphatases and Specificity in Various Cell Models of Metabolic Disturbances.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Feb 9;17(2):229. doi: 10.3390/ph17020229. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas Update 2012. [Accessed 4 April 2013];2013 at http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas/5e/Update2012.
-
- Perley M, Kipnis DM. Plasma insulin responses to glucose and tolbutamide of normal weight and obese diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1966;15:867–874. - PubMed
-
- Himsworth HP. Diabetes mellitus: its differentiation into insulin-sensitive and insulin-insensitive types. Lancet. 1936;227:127–130. - PubMed
-
- Reaven GM. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988;37:1595–1607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

