Evaluation of the effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on cultured Rana catesbeiana tailfin tissue
- PMID: 24312126
- PMCID: PMC3836013
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00251
Evaluation of the effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on cultured Rana catesbeiana tailfin tissue
Abstract
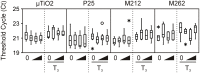
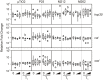
Nanoparticles (NPs), materials that have one dimension less than 100 nm, are used in manufacturing, health, and food products, and consumer products including cosmetics, clothing, and household appliances. Their utility to industry is derived from their high surface-area-to-volume ratios and physico-chemical properties distinct from their bulk counterparts, but the near-certainty that NPs will be released into the environment raises the possibility that they could present health risks to humans and wildlife. The thyroid hormones (THs), thyroxine, and 3,3',5-triiodothyronine (T3), are involved in development and metabolism in vertebrates including humans and frogs. Many of the processes of anuran metamorphosis are analogous to human post-embryonic development and disruption of TH action can have drastic effects. These shared features make the metamorphosis of anurans an excellent model for screening for endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs). We used the cultured tailfin (C-fin) assay to examine the exposure effects of 0.1-10 nM (~8-800 ng/L) of three types of ~20 nm TiO2 NPs (P25, M212, M262) and micron-sized TiO2 (μ TiO2) ±10 nM T3. The actual Ti levels were 40.9-64.7% of the nominal value. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (QPCR) was used to measure the relative amounts of mRNA transcripts encoding TH-responsive THs receptors (thra and thrb) and Rana larval keratin type I (rlk1), as well as the cellular stress-responsive heat shock protein 30 kDa (hsp30), superoxide dismutase (sod), and catalase (cat). The levels of the TH-responsive transcripts were largely unaffected by any form of TiO2. Some significant effects on stress-related transcripts were observed upon exposure to micron-sized TiO2, P25, and M212 while no effect was observed with M262 exposure. Therefore, the risk of adversely affecting amphibian tissue by disrupting TH-signaling or inducing cellular stress is low for these compounds relative to other previously-tested NPs.
Keywords: amphibian; nanometal; nanoparticle; organ culture; oxidative stress; thyroid hormone; titanium dioxide.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of transcriptome responses of the liver, tail fin, and olfactory epithelium of Rana [Lithobates] catesbeiana tadpoles disrupted by thyroid hormones and estrogen.Aquat Toxicol. 2022 Dec;253:106344. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2022.106344. Epub 2022 Oct 29. Aquat Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36334376
-
Transcriptomics investigation of thyroid hormone disruption in the olfactory system of the Rana [Lithobates] catesbeiana tadpole.Aquat Toxicol. 2018 Sep;202:46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.06.015. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Aquat Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30007154
-
Dioctyl Sodium Sulfosuccinate as a Potential Endocrine Disruptor of Thyroid Hormone Activity in American bullfrog, Rana (Lithobates) catesbeiana, Tadpoles.Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2021 May;80(4):726-734. doi: 10.1007/s00244-021-00835-1. Epub 2021 Mar 28. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33774695
-
Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: a Risk for Human Health?Mini Rev Med Chem. 2016;16(9):762-9. doi: 10.2174/1389557516666160321114341. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26996620 Review.
-
Influence of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Human Health and the Environment.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Sep 10;11(9):2354. doi: 10.3390/nano11092354. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34578667 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reactive oxygen species and other biochemical and morphological biomarkers in the gills and kidneys of the Neotropical freshwater fish, Prochilodus lineatus, exposed to titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Aug;25(23):22963-22976. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2393-4. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29858996
-
Contaminant and Environmental Influences on Thyroid Hormone Action in Amphibian Metamorphosis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 May 14;10:276. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00276. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31156547 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bolis V., Busco C., Ciarletta M., Distasi C., Erriquez J., Fenoglio I., et al. (2012). Hydrophilic/hydrophobic features of TiO2 nanoparticles as a function of crystal phase, surface area and coating, in relation to their potential toxicity in peripheral nervous system. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 369, 28–39 10.1016/j.jcis.2011.11.058 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cermenati L., Pichat P., Guillard C., Albini A. (1997). Probing the TiO2 photocatalytic mechanisms in water purification by use of quinoline, photo-fenton generated OH. radicals and superoxide dismutase. J. Phys. Chem. B 101, 2650–2658 10.1021/jp962700p - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

