Exploring the correlation between lipid packaging in lipoplexes and their transfection efficacy
- PMID: 24309311
- PMCID: PMC3857061
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics3040848
Exploring the correlation between lipid packaging in lipoplexes and their transfection efficacy
Abstract
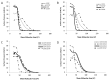
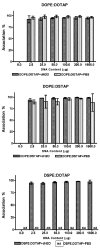
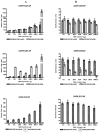
Whilst there is a large body of evidence looking at the design of cationic liposomes as transfection agents, correlates of formulation to function remain elusive. In this research, we investigate if lipid packaging can give further insights into transfection efficacy. DNA lipoplexes composed of 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DOPE) or 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DSPE) in combination with 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane (DOTAP) or 1,2-stearoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane (DSTAP) were prepared by the lipid hydration method. Each of the formulations was prepared by hydration in dH2O or phosphate buffer saline (PBS) to investigate the effect of buffer salts on lipoplex physicochemical characteristics and in vitro transfection. In addition, Langmuir monolayer studies were performed to investigate any possible correlation between lipid packaging and liposome attributes. Using PBS, rather than dH2O, to prepare the lipoplexes increased the size of vesicles in most of formulations and resulted in variation in transfection efficacies. However, one combination of lipids (DSPE:DOTAP) could not form liposomes in PBS, whilst the DSPE:DSTAP combination could not form liposomes in either aqueous media. Monolayer studies demonstrated saturated lipid combinations offered dramatically closer molecular packing compared to the other combinations which could suggest why this lipid combination could not form vesicles. Of the lipoplexes prepared, those formulated with DSTAP showed higher transfection efficacy, however, the effect of buffer on transfection efficiency was formulation dependent.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to improve smoking cessation rates in primary care.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 6;9(9):CD011556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34693994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Treatment options for patients with pilonidal sinus disease: PITSTOP, a mixed-methods evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jul;28(33):1-113. doi: 10.3310/KFDQ2017. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39045854 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Di-Peptide-Modified Gemini Surfactants as Gene Delivery Vectors: Exploring the Role of the Alkyl Tail in Their Physicochemical Behavior and Biological Activity.AAPS J. 2016 Sep;18(5):1168-1181. doi: 10.1208/s12248-016-9906-1. Epub 2016 May 16. AAPS J. 2016. PMID: 27184577
-
Effect of PEGylation on Ligand-Targeted Magnetoliposomes: A Missed Goal.ACS Omega. 2017 Oct 31;2(10):6544-6555. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b00778. Epub 2017 Oct 9. ACS Omega. 2017. PMID: 30023523 Free PMC article.
-
Smart Lipid-Based Nanosystems for Therapeutic Immune Induction against Cancers: Perspectives and Outlooks.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 23;14(1):26. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010026. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 35056922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Efficient Lipid-Based Delivery Systems Enable a Delayed Uptake and Sustained Expression of mRNA in Human Cells and Mouse Tissues.Pharmaceutics. 2024 May 19;16(5):684. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16050684. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38794346 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of novel cationic gene based liposomes with cyclodextrin prepared by thin film hydration and microfluidic systems.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 22;9(1):15120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51065-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31641141 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sulivan S.M. Inroduction to gene therapy and guidlines to pharmaceutical development. In: Rolland A., Sulivan S.M., editors. Pharmaceutical Gene Delivery. 1st ed. Marcel Decker, Inc; New York, NY, USA: 2003.
-
- Vassaux G., Nitcheu J., Jezzard S., Lemoine N.R. Bacterial gene therapy strategies. J. Pathol. 2006;208:290–298. - PubMed
-
- Lul V.W., Haung L. Nonviral approaches for cancer gene therapy. In: Rolland A., Sulivan S.M., editors. Pharmaceutical Gene Delivery Systems. 1st ed. Marcel Dekker, Inc.; New York, NY, USA: 2003. pp. 279–319.
-
- Gregoriadis G., Bacon A., Caparros-Wanderley W., McCormack B. A role for liposomes in genetic vaccination. Vaccine. 2002;20(Suppl 5):B1–B9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

