mtDNA Mutations and Their Role in Aging, Diseases and Forensic Sciences
- PMID: 24307969
- PMCID: PMC3843653
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2013.0400364
mtDNA Mutations and Their Role in Aging, Diseases and Forensic Sciences
Abstract
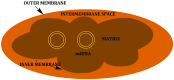
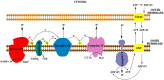
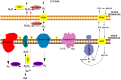
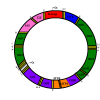
Mitochondria are independent organelles with their own DNA. As a primary function, mitochondria produce the energy for the cell through Oxidative Phosphorylation (OXPHOS) in the Electron Transport Chain (ETC). One of the toxic products of this process is Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), which can induce oxidative damage in macromolecules like lipids, proteins and DNA. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is less protected and has fewer reparation mechanisms than nuclear DNA (nDNA), and as such is more exposed to oxidative, mutation-inducing damage. This review analyzes the causes and consequences of mtDNA mutations and their relationship with the aging process. Neurodegenerative diseases, related with the aging, are consequences of mtDNA mutations resulting in a decrease in mitochondrial function. Also described are "mitochondrial diseases", pathologies produced by mtDNA mutations and whose symptoms are related with mitochondrial dysfunction. Finally, mtDNA haplogroups are defined in this review; these groups are important for determination of geographical origin of an individual. Additionally, different haplogroups exhibit variably longevity and risk of certain diseases. mtDNA mutations in aging and haplogroups are of special interest to forensic science research. Therefore this review will help to clarify the key role of mtDNA mutations in these processes and support further research in this area.
Keywords: Aging; Diseases; Electron Transport Chain (ETC); Forensic Sciences; Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA); Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795
-
Significance of Mitochondria DNA Mutations in Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1038:219-230. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-6674-0_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29178079 Review.
-
A mitochondrial paradigm for degenerative diseases and ageing.Novartis Found Symp. 2001;235:247-63; discussion 263-6. doi: 10.1002/0470868694.ch20. Novartis Found Symp. 2001. PMID: 11280029 Review.
-
The mitochondrial genome in human adaptive radiation and disease: on the road to therapeutics and performance enhancement.Gene. 2005 Jul 18;354:169-80. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.05.001. Gene. 2005. PMID: 16024186 Review.
-
Targeting Mitochondrial Function with Chemoptogenetics.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 1;10(10):2459. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102459. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289721 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional genomic analysis reveals overlapping and distinct features of chronologically long-lived yeast populations.Aging (Albany NY). 2015 Mar;7(3):177-94. doi: 10.18632/aging.100729. Aging (Albany NY). 2015. PMID: 25769345 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity of nanotitanium dioxide (TiO2-NP) on human monocytes and their mitochondria.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Mar;25(7):6739-6750. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0974-2. Epub 2017 Dec 20. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29260482
-
Oxidative Modification and Its Implications for the Neurodegeneration of Parkinson's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Mar;54(2):1404-1418. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9743-3. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26843115 Review.
-
Connection Between HIV and Mitochondria in Cardiovascular Disease and Implications for Treatments.Circ Res. 2024 May 24;134(11):1581-1606. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.124.324296. Epub 2024 May 23. Circ Res. 2024. PMID: 38781302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Testosterone enhances mitochondrial complex V function in the substantia nigra of aged male rats.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 May 23;12(11):10398-10414. doi: 10.18632/aging.103265. Epub 2020 May 23. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32445551 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
