Mechanisms of heterosynaptic metaplasticity
- PMID: 24298150
- PMCID: PMC3843880
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0148
Mechanisms of heterosynaptic metaplasticity
Abstract
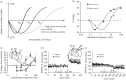
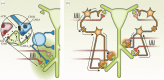
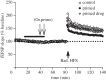
Synaptic plasticity is fundamental to the neural processes underlying learning and memory. Interestingly, synaptic plasticity itself can be dynamically regulated by prior activity, in a process termed 'metaplasticity', which can be expressed both homosynaptically and heterosynaptically. Here, we focus on heterosynaptic metaplasticity, particularly long-range interactions between synapses spread across dendritic compartments, and review evidence for intracellular versus intercellular signalling pathways leading to this effect. Of particular interest is our previously reported finding that priming stimulation in stratum oriens of area CA1 in the hippocampal slice heterosynaptically inhibits subsequent long-term potentiation and facilitates long-term depression in stratum radiatum. As we have excluded the most likely intracellular signalling pathways that might mediate this long-range heterosynaptic effect, we consider the hypothesis that intercellular communication may be critically involved. This hypothesis is supported by the finding that extracellular ATP hydrolysis, and activation of adenosine A2 receptors are required to induce the metaplastic state. Moreover, delivery of the priming stimulation in stratum oriens elicited astrocytic calcium responses in stratum radiatum. Both the astrocytic responses and the metaplasticity were blocked by gap junction inhibitors. Taken together, these findings support a novel intercellular communication system, possibly involving astrocytes, being required for this type of heterosynaptic metaplasticity.
Keywords: astrocytes; gap junctions; intercellular signalling; long-term depression; long-term potentiation; metaplasticity.
Figures
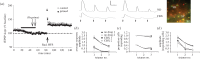
Similar articles
-
Purinergic receptor- and gap junction-mediated intercellular signalling as a mechanism of heterosynaptic metaplasticity.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2013 Oct;105:31-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.05.010. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2013. PMID: 23747410
-
Calcium-dependent but action potential-independent BCM-like metaplasticity in the hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2012 May 16;32(20):6785-94. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0634-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22593048 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Mediated Metaplastic Inhibition of LTP Is Constitutively Engaged in an Alzheimer's Disease Model.J Neurosci. 2019 Nov 13;39(46):9083-9097. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1492-19.2019. Epub 2019 Sep 30. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31570539 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes-, stress- and ageing-related changes in synaptic plasticity in hippocampus and neocortex--the same metaplastic process?Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 May 6;585(1):153-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.11.084. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18395200 Review.
-
Multiple forms of metaplasticity at a single hippocampal synapse during late postnatal development.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2015 Apr;12:145-54. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2015.01.009. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25752732 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diversity of Astroglial Effects on Aging- and Experience-Related Cortical Metaplasticity.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Jul 13;11:239. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00239. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30057525 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Synaptic Microcircuits in the Mushroom Bodies of the Honeybee.Insects. 2020 Jan 7;11(1):43. doi: 10.3390/insects11010043. Insects. 2020. PMID: 31936165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remote muscle priming anodal transcranial direct current stimulation attenuates short interval intracortical inhibition and increases time to task failure of a constant workload cycling exercise.Exp Brain Res. 2021 Jun;239(6):1975-1985. doi: 10.1007/s00221-021-06103-x. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Exp Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33891144
-
Foxa1 mediates eccrine sweat gland development through transcriptional regulation of Na-K-ATPase expression.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2022 Aug 15;55:e12149. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2022e12149. eCollection 2022. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2022. PMID: 35976271 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between global and pathway-specific synaptic plasticity in CA1 pyramidal cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 6;7(1):17040. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17161-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29213058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Migaud M, et al. 1998. Enhanced long-term potentiation and impaired learning in mice with mutant postsynaptic density-95 protein. Nature 396, 433–439 (doi:10.1038/24790) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abraham WC. 2008. Metaplasticity: tuning synapses and networks for plasticity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 387–399 (doi:10.1038/nrn2356) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abraham WC, Bear MF. 1996. Metaplasticity: the plasticity of synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 19, 126–130 (doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(96)80018-X) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

