Th17 and Th22 cells in psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis
- PMID: 24286492
- PMCID: PMC3978433
- DOI: 10.1186/ar4317
Th17 and Th22 cells in psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of this study was to characterize interleukin 17 (IL-17) and interleukin 22 (IL-22) producing cells in peripheral blood (PB), skin, synovial fluid (SF) and synovial tissue (ST) in patients with psoriasis (Ps) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Methods: Flow cytometry was used to enumerate cells making IL-22 and IL-17, in skin and/or SF and PB from 11 patients with Ps and 12 patients with PsA; skin and PB of 15 healthy controls and SF from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients were used as controls. Expression of the interleukin 23 receptor (IL-23R) and chemokine receptors CCR4 and CCR6 was examined. Secretion of IL-17 and IL-22 was measured by ELISA. ST was analysed by immunohistochemical staining of IL-17 and IL-22.
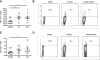
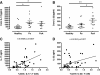
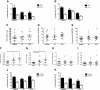
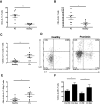
Results: Increased frequencies of IL-17+ and IL-22+ CD4+ T cells were seen in PB of patients with PsA and Ps. IL-17 secretion was significantly elevated in both PsA and Ps, whilst IL-22 secretion was higher in PsA compared to Ps and healthy controls. A higher proportion of the CD4+ cells making IL-17 or IL-22 expressed IL-23R and frequencies of IL-17+, CCR6+ and CCR4+ T cells were elevated in patients with Ps and those with PsA. In patients with PsA, CCR6+ and IL-23R + T cells numbers were elevated in SF compared to PB. Increased frequencies of IL-17+ and IL-22+ CD4+ T cells were demonstrated in Ps skin lesions. In contrast, whilst elevated frequencies of CD4+ IL-17+ cells were seen in PsA SF compared to PB, frequencies of CD4+ IL-22+ T cells were lower. Whereas IL-17 expression was equivalent in PsA, osteoarthritis (OA) and RA ST, IL-22 expression was higher in RA than either OA or PsA ST, in which IL-22 was strikingly absent.
Conclusions: Elevated frequencies of IL-17 and IL-22 producing CD4+ T cells were a feature of both Ps and PsA. However their differing distribution at disease sites, including lower frequencies of IL-22+ CD4+ T cells in SF compared to skin and PB, and lack of IL-22 expression in ST suggests that Th17 and Th22 cells have common, as well as divergent roles in the pathogenesis of Ps and PsA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tissue-Resident Memory CD8+ T Cells From Skin Differentiate Psoriatic Arthritis From Psoriasis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Jul;73(7):1220-1232. doi: 10.1002/art.41652. Epub 2021 May 25. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33452865 Free PMC article.
-
JAK/STAT/PKCδ molecular pathways in synovial fluid T lymphocytes reflect the in vivo T helper-17 expansion in psoriatic arthritis.Immunol Res. 2014 Jan;58(1):61-9. doi: 10.1007/s12026-013-8481-0. Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 24385089
-
Brief report: enrichment of activated group 3 innate lymphoid cells in psoriatic arthritis synovial fluid.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 Oct;67(10):2673-8. doi: 10.1002/art.39261. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26137857
-
Are psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis the same disease? The IL-23/IL-17 axis data.Autoimmun Rev. 2017 Jan;16(1):10-15. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2016.09.015. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Autoimmun Rev. 2017. PMID: 27666819 Review.
-
Role of IL-17 in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013 Apr;44(2):183-93. doi: 10.1007/s12016-012-8307-1. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22362575 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of podoplanin in the high interleukin-17A secretion resulting from interactions between activated lymphocytes and psoriatic skin-derived mesenchymal cells.Clin Exp Immunol. 2016 Oct;186(1):64-74. doi: 10.1111/cei.12830. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27328392 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting interleukin-17 in chronic inflammatory disease: A clinical perspective.J Exp Med. 2020 Jan 6;217(1):e20191123. doi: 10.1084/jem.20191123. J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 31727781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pemphigus foliaceus patients (Fogo Selvagem) treated with kinesiotherapy presented lower levels of proinflammatory cytokines.J Exerc Rehabil. 2019 Jun 30;15(3):460-467. doi: 10.12965/jer.1938146.073. eCollection 2019 Jun. J Exerc Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 31316942 Free PMC article.
-
A catalog of potential putative functional variants in psoriasis genome-wide association regions.PLoS One. 2018 May 1;13(5):e0196635. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196635. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29715312 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of arthroscopic guided synovial biopsy in understanding synovial tissue pathology in health and disease states.World J Orthop. 2014 Nov 18;5(5):566-73. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v5.i5.566. eCollection 2014 Nov 18. World J Orthop. 2014. PMID: 25405084 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Menter A, Gottlieb A, Feldman SR, Van Voorhees AS, Leonardi CL, Gordon KB, Lebwohl M, Koo JY, Elmets CA, Korman NJ, Beutner KR, Bhushan R. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: Section 1. Overview of psoriasis and guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;15:826–850. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2008.02.039. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sieper J, Rudwaleit M, Baraliakos X, Brandt J, Braun J, Burgos-Vargas R, Dougados M, Hermann KG, Landewé R, Maksymowych W, van der Heijde D. The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) handbook: a guide to assess spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;15(Suppl 2):ii1–ii44. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.104018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

