Hypoxia-induced factor-1 alpha upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor C to promote lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis in breast cancer patients
- PMID: 24285946
- PMCID: PMC3841473
- DOI: 10.7555/JBR.27.20130021
Hypoxia-induced factor-1 alpha upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor C to promote lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis in breast cancer patients
Abstract
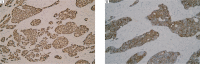
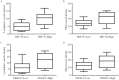
Hypoxia-induced factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) affects many effector molecules and regulates tumor lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis during hypoxia. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of HIF-1α in the regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) expression and its effect on lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis in breast cancer. Lymphatic vessel density (LVD), microvessel density (MVD) and the expressions of HIF-1α and VEGF-C proteins were evaluated by immunohistochemistry in 75 breast cancer samples. There was a significant correlation between HIF-1α and VEGF-C (P = 0.014, r = 0.273, Spearman's coefficient of correlation). HIF-1α and VEGF-C overexpression was significantly correlated with higher LVD (P = 0.003 and P = 0.017, respectively), regional lymph nodal involvement (P = 0.002 and P = 0.004, respectively) and advanced tumor, node, metastasis (TNM) classification (P = 0.001 and P = 0.01, respectively). Higher MVD was observed in the group expressing higher levels of HIF-1α and VEGF-C (P = 0.033 and P = 0.037, respectively). Univariate analysis showed shorter survival time in patients expressing higher levels of HIF-1α and VEGF-C. HIF-1α was also found to be an independent prognostic factor of overall survival in multivariate analysis. The results suggest that HIF-1α may affect VEGF-C expression, thus acting as a crucial regulator of lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis in breast cancer. This study highlights promising potential of HIF-1α as a therapeutic target against tumor lymph node metastasis.
Keywords: HIF-1α; VEGF-C; angiogenesis; breast cancer; lymphangiogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported no conflict of interests.
Figures

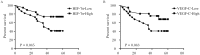
Similar articles
-
Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha correlates with VEGF-C expression and lymphangiogenesis in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006 Sep;99(2):135-41. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9190-3. Epub 2006 Mar 23. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006. PMID: 16555123
-
Hypoxia inducible factor-alpha expression correlates with vascular endothelial growth factor-C expression and lymphangiogenesis/angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2008 May-Jun;28(3A):1659-66. Anticancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18630523
-
Effect of HIF-1alpha on VEGF-C induced lymphangiogenesis and lymph nodes metastases of pancreatic cancer.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2006;26(5):562-4. doi: 10.1007/s11596-006-0520-9. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2006. PMID: 17219968
-
Doxorubicin induced immune abnormalities and inflammatory responses via HMGB1, HIF1-α and VEGF pathway in progressive of cardiovascular damage.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Mar 21;76:103501. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103501. eCollection 2022 Apr. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35340325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Ligands and Receptors in Breast Cancer.J Clin Med. 2023 Mar 21;12(6):2412. doi: 10.3390/jcm12062412. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36983412 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Significance of High VEGF-C Expression for Patients with Breast Cancer: An Update Meta Analysis.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 3;11(11):e0165725. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165725. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27812168 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of metabolic enzyme pyruvate kinase M2 in breast cancer: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Nov;96(46):e8690. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008690. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29145305 Free PMC article.
-
Both high expression of pyruvate kinase M2 and vascular endothelial growth factor-C predicts poorer prognosis in human breast cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jul 1;8(7):8028-37. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26339369 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of cluster of differentiation 34 and vascular endothelial growth factor in breast cancer, and their prognostic significance.Oncol Lett. 2015 Aug;10(2):723-729. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3348. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26622560 Free PMC article.
-
GRK2-Dependent HuR Phosphorylation Regulates HIF1α Activation under Hypoxia or Adrenergic Stress.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 13;12(5):1216. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051216. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32413989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Padera TP, Kadambi A, di Tomaso E, Carreira CM, Brown EB, Boucher Y, et al. Lymphatic metastasis in the absence of functional intratumor lymphatics. Science. 2002;296:1883–6. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi M, Yoshimoto T, Kubo H. Molecular mechanisms of lymphangiogenesis. Int J Hematol. 2004;80:29–34. - PubMed
-
- Lin J, Lalani AS, Harding TC, Gonzalez M, Wu WW, Luan B, et al. Inhibition of lymphogenous metastasis using adeno-associated virus-mediated gene transfer of a soluble VEGFR-3 decoy receptor. Cancer Res. 2005;65:6901–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

