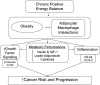
Interacting inflammatory and growth factor signals underlie the obesity-cancer link
- PMID: 24285690
- PMCID: PMC3901418
- DOI: 10.3945/jn.113.178533
Interacting inflammatory and growth factor signals underlie the obesity-cancer link
Abstract
The prevalence of obesity, an established risk factor for many chronic diseases (including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and several types of cancer), has risen steadily for the past several decades in the United States and many parts of the world. Today, ∼70% of U.S. adults and 30% of children are at an unhealthy weight. The evidence on key biologic mechanisms underlying the obesity-cancer link, with an emphasis on local and systemic inflammatory processes and their crosstalk with energy-sensing growth factor signaling pathways, will be discussed. Understanding the influence and underlying mechanisms of obesity on chronic inflammation and cancer will identify promising mechanistic targets and strategies for disrupting the obesity-cancer link and provide important lessons regarding the associations between obesity, inflammation, and other chronic diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosures: L. M. Lashinger, N. A. Ford, and S. D. Hursting, no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The growing challenge of obesity and cancer: an inflammatory issue.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011 Jul;1229:45-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06096.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011. PMID: 21793838 Review.
-
Growth signals, inflammation, and vascular perturbations: mechanistic links between obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cancer.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Aug;32(8):1766-70. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.241927. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22815342 Review.
-
Reducing the weight of cancer: mechanistic targets for breaking the obesity-carcinogenesis link.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Aug;22(4):659-69. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2008.08.009. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008. PMID: 18971125 Review.
-
Cardiovascular diseases and metabolic abnormalities associated with obesity: What is the role of inflammatory responses? A systematic review.Microvasc Res. 2020 Sep;131:104023. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2020.104023. Epub 2020 May 30. Microvasc Res. 2020. PMID: 32485192
-
Obesity and resistance to cancer chemotherapy: interacting roles of inflammation and metabolic dysregulation.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Oct;96(4):458-63. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2014.136. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24960521 Review.
Cited by
-
Combating osteoporosis and obesity with exercise: leveraging cell mechanosensitivity.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019 Jun;15(6):339-355. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0170-1. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30814687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk determination and prevention of breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Sep 28;16(5):446. doi: 10.1186/s13058-014-0446-2. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25467785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of a polyphenol-enriched preparation on chemoprevention of mammary carcinoma through cancer stem cells and inflammatory pathways modulation.J Transl Med. 2016 Jan 14;14:13. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0770-7. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 26762586 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin signaling molecular actions and drug target in hepatocellular carcinoma.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Nov 14;8:2295-302. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S69004. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25484575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity and cancer: mechanistic insights from transdisciplinary studies.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015 Dec;22(6):R365-86. doi: 10.1530/ERC-15-0400. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26373570 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass index among US adults, 1999–2010. JAMA. 2012;307:491–7 - PubMed
-
- Hossain P, Kawar B, El Nahas M. Obesity and diabetes in the developing world—a growing challenge. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:213–5 - PubMed
-
- Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1625–38 - PubMed
-
- van Kruijsdijk RC, van der Wall E, Visseren FL. Obesity and cancer: the role of dysfunctional adipose tissue. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18:2569–78 - PubMed
-
- Calle EE, Kaaks R. Overweight, obesity and cancer: epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:579–91 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous