Integration of signals generated by nutrients, hormones, and exercise in skeletal muscle
- PMID: 24284445
- PMCID: PMC3862457
- DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.113.068387
Integration of signals generated by nutrients, hormones, and exercise in skeletal muscle
Abstract
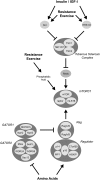
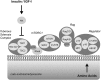
This review focuses on anabolic signaling pathways through which insulin, amino acids, and resistance exercise act to regulate the protein kinase complex referred to as mechanistic target of rapamycin complex (mTORC) 1. Initially, individual pathways through which the 3 anabolic signals act to modulate mTORC1 signaling will be discussed, followed by a summation of evidence showing an additive effect of the regulators. The emphasis will be on mTORC1 signaling in skeletal muscle and its contribution to modulation of rates of protein synthesis. In addition, results from studies using cells in culture will be used to provide a more complete picture of the molecular details of the individual pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nutrient-induced stimulation of protein synthesis in mouse skeletal muscle is limited by the mTORC1 repressor REDD1.J Nutr. 2015 Apr;145(4):708-13. doi: 10.3945/jn.114.207621. Epub 2015 Feb 25. J Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25716553 Free PMC article.
-
Differential contribution of insulin and amino acids to the mTORC1-autophagy pathway in the liver and muscle.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 19;288(29):21074-21081. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.456228. Epub 2013 Jun 6. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23744068 Free PMC article.
-
Amino Acids Attenuate Insulin Action on Gluconeogenesis and Promote Fatty Acid Biosynthesis via mTORC1 Signaling Pathway in trout Hepatocytes.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(3):1084-100. doi: 10.1159/000430281. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26112996
-
Regulation of mTORC1 by growth factors, energy status, amino acids and mechanical stimuli at a glance.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2016 Mar 1;13:8. doi: 10.1186/s12970-016-0118-y. eCollection 2016. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26937223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amino acid sensing and activation of mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1: implications for skeletal muscle.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2016 Jan;19(1):67-73. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000240. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2016. PMID: 26560525 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia Impairs Muscle Function and Reduces Myotube Size in Tissue Engineered Skeletal Muscle.J Cell Biochem. 2017 Sep;118(9):2599-2605. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25982. Epub 2017 May 15. J Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28294416 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity Alters the Muscle Protein Synthetic Response to Nutrition and Exercise.Front Nutr. 2019 Jun 13;6:87. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2019.00087. eCollection 2019. Front Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31263701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of prolonged leucine supplementation on protein synthesis and lean growth in neonatal pigs.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Sep 15;309(6):E601-10. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00089.2015. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26374843 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between Growth of Muscle and Stature: Mechanisms Involved and Their Nutritional Sensitivity to Dietary Protein: The Protein-Stat Revisited.Nutrients. 2021 Feb 25;13(3):729. doi: 10.3390/nu13030729. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33668846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Skeletal Muscle Protein Metabolism Responses to Amino Acid Nutrition.Adv Nutr. 2016 Jul 15;7(4):828S-38S. doi: 10.3945/an.115.011650. Print 2016 Jul. Adv Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27422520 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bracho-Valdés I, Moreno-Alvarez P, Valencia-Martinez I, Robles-Molina E, Chavez-Vargas L, Vazquez-Prado J. mTORC1- and mTORC2-interacting proteins keep their multifunctional partners focused. IUBMB Life 2011;63:896–914. - PubMed
-
- Dempsey JM, Mahoney SJ, Blenis J. mTORC1-mediated control of protein translation. In: Fuyuhiko T, Michael NH, eds. The enzymes. Waltham, MA: Academic Press, 2010:1–20.
-
- Marcotrigiano J, Gingras A-C, Sonenberg N, Burley SK. Cap-dependent translation initiation in eukaryotes is regulated by a molecular mimic of eIF4G. Mol Cell 1999;3:707–16. - PubMed
-
- Holz MK, Blenis J. Identification of S6K1 as a novel mTOR-phosphorylating kinase. J Biol Chem 2005;280:26089–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

