MicroRNAs as Molecular Targets for Cancer Therapy: On the Modulation of MicroRNA Expression
- PMID: 24275848
- PMCID: PMC3817605
- DOI: 10.3390/ph6101195
MicroRNAs as Molecular Targets for Cancer Therapy: On the Modulation of MicroRNA Expression
Abstract
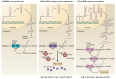
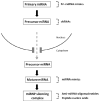
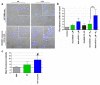
The discovery of small RNA molecules with the capacity to regulate messenger RNA (mRNA) stability and translation (and consequently protein synthesis) has revealed an additional level of post-transcriptional gene control. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), an evolutionarily conserved class of small noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally by base pairing to complementary sequences in the 3' untranslated regions of target mRNAs, are part of this modulatory RNA network playing a pivotal role in cell fate. Functional studies indicate that miRNAs are involved in the regulation of almost every biological pathway, while changes in miRNA expression are associated with several human pathologies, including cancer. By targeting oncogenes and tumor suppressors, miRNAs have the ability to modulate key cellular processes that define the cell phenotype, making them highly promising therapeutic targets. Over the last few years, miRNA-based anti-cancer therapeutic approaches have been exploited, either alone or in combination with standard targeted therapies, aiming at enhancing tumor cell killing and, ideally, promoting tumor regression and disease remission. Here we provide an overview on the involvement of miRNAs in cancer pathology, emphasizing the mechanisms of miRNA regulation. Strategies for modulating miRNA expression are presented and illustrated with representative examples of their application in a therapeutic context.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression profile of MicroRNA: An Emerging Hallmark of Cancer.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(6):642-653. doi: 10.2174/1386207322666190325122821. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 30914015 Review.
-
MicroRNAs: non coding pleiotropic factors in development, cancer prevention and treatment.Microrna. 2013;2(2):81. doi: 10.2174/2211536611302020001. Microrna. 2013. PMID: 25070777
-
Small non-coding RNAs as novel therapeutics.Curr Mol Med. 2010 Jun;10(4):361-8. doi: 10.2174/156652410791317048. Curr Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20455856 Review.
-
Shielding the messenger (RNA): microRNA-based anticancer therapies.Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Jul;131(1):18-32. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.04.006. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Pharmacol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21514318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human microRNA oncogenes and tumor suppressors show significantly different biological patterns: from functions to targets.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 30;5(9):e13067. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013067. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20927335 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
MiR-200b expression in breast cancer: a prognostic marker and act on cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting Sp1.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Apr;19(4):760-9. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12432. Epub 2015 Jan 30. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25639535 Free PMC article.
-
The various role of microRNAs in breast cancer angiogenesis, with a special focus on novel miRNA-based delivery strategies.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Feb 10;23(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02837-y. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 36765409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of associations between small molecule drugs and miRNAs based on functional similarity.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 21;7(25):38658-38669. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9577. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27232942 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-130a-3p blocks Wnt signaling cascade in the triple-negative breast cancer by targeting the key players at multiple points.Heliyon. 2020 Nov 9;6(11):e05434. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05434. eCollection 2020 Nov. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33225091 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of therapeutic miRNA using polymer-based formulation.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019 Dec;9(6):1043-1056. doi: 10.1007/s13346-019-00645-y. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31049843 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

