Serum microRNA-21 levels are related to tumor size in gastric cancer patients but cannot predict prognosis
- PMID: 24260069
- PMCID: PMC3834305
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2013.1626
Serum microRNA-21 levels are related to tumor size in gastric cancer patients but cannot predict prognosis
Abstract
In patients with gastric cancer (GC), circulating microRNA-21 (miR-21) is overexpressed and may serve as a diagnostic biomarker. In the present study, it was hypothesized that the serum miR-21 expression levels were associated with prognosis in the patients with GC. The expression levels of serum miR-21 were measured using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assays in 103 GC patients. Survival and Cox proportional-hazards regression analyses were performed to determine the correlation between serum miR-21 expression levels and prognosis in the patients. The correlation between the serum miR-21 levels and the clinicopathological factors of the patients was also analyzed. Survival curves were not significantly different between the groups exhibiting high and low levels of serum miR-21 expression. High levels of miR-21 in the serum were associated with an increased tumor size and an advanced pT stage. These findings suggest that serum miR-21 could be exploited as a practical biomarker for monitoring tumor burden in patients with GC.
Keywords: biomarker; microRNA-21; prognosis; stomach neoplasma.
Figures

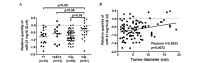
Similar articles
-
Clinical significance of serum miR-25 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in human gastric cancer.Cancer Biomark. 2019;24(4):477-483. doi: 10.3233/CBM-182213. Cancer Biomark. 2019. PMID: 30909187
-
Serum miR-200c expression level as a prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer.Genet Mol Res. 2015 Dec 7;14(4):15913-20. doi: 10.4238/2015.December.7.2. Genet Mol Res. 2015. PMID: 26662382
-
Down-regulated serum miR-126 is associated with aggressive progression and poor prognosis of gastric cancer.Cancer Biomark. 2018;22(1):119-126. doi: 10.3233/CBM-171099. Cancer Biomark. 2018. PMID: 29562500
-
Circulating microRNA-203 predicts metastases, early recurrence, and poor prognosis in human gastric cancer.Gastric Cancer. 2016 Jul;19(3):744-53. doi: 10.1007/s10120-015-0521-0. Epub 2015 Aug 2. Gastric Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26233325
-
MiR-1236-3p serves as a new diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer.Cancer Biomark. 2019;25(2):127-132. doi: 10.3233/CBM-171026. Cancer Biomark. 2019. PMID: 31045511
Cited by
-
Prognostic role of microRNA-21 in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis.Med Sci Monit. 2014 Sep 18;20:1668-74. doi: 10.12659/MSM.892096. Med Sci Monit. 2014. PMID: 25230738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
May Circulating microRNAs be Gastric Cancer Diagnostic Biomarkers?J Cancer. 2015 Sep 20;6(12):1206-13. doi: 10.7150/jca.12535. eCollection 2015. J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26535061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR‑21‑5p confers doxorubicin resistance in gastric cancer cells by targeting PTEN and TIMP3.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Apr;41(4):1855-1866. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3405. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29393355 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of miR-203 induced by Helicobacter pylori infection promotes the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by targeting CASK.Oncotarget. 2014 Nov 30;5(22):11631-40. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2600. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25373785 Free PMC article.
-
The Profile of Serum microRNAs Predicts Prognosis for Resected Gastric Cancer Patients Receiving Platinum-Based Chemotherapy.Dig Dis Sci. 2017 May;62(5):1223-1234. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4513-2. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Dig Dis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28341869
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Huang Y, Shen XJ, Zou Q, Wang SP, Tang SM, Zhang GZ. Biological functions of microRNAs: a review. J Physiol Biochem. 2011;67:129–139. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008;18:997–1006. - PubMed
-
- Huang Z, Huang D, Ni S, Peng Z, Sheng W, Du X. Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:118–126. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
