Methionine sulfoxide reductases protect against oxidative stress in Staphylococcus aureus encountering exogenous oxidants and human neutrophils
- PMID: 24247266
- PMCID: PMC3972283
- DOI: 10.1159/000355915
Methionine sulfoxide reductases protect against oxidative stress in Staphylococcus aureus encountering exogenous oxidants and human neutrophils
Abstract
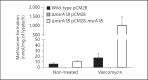
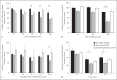
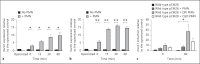
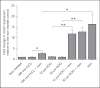
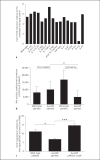
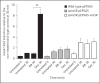
To establish infection successfully, Staphylococcus aureus must evade clearance by polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN). We studied the expression and regulation of the methionine sulfoxide reductases (Msr) that are involved in the repair of oxidized staphylococcal proteins and investigated their influence on the fate of S. aureus exposed to oxidants or PMN. We evaluated a mutant deficient in msrA1 and msrB for susceptibility to hydrogen peroxide, hypochlorous acid and PMN. The expression of msrA1 in wild-type bacteria ingested by human PMN was assessed by real-time PCR. The regulation of msr was studied by screening a library of two-component regulatory system (TCS) mutants for altered msr responses. Relative to the wild-type bacteria, bacteria deficient in Msr were more susceptible to oxidants and PMN. Upregulation of staphylococcal msrA1 occurred within the phagosomes of normal PMN and PMN deficient in NADPH oxidase activity. Furthermore, PMN granule-rich extract stimulated the upregulation of msrA1. Modulation of msrA1 within PMN was shown to be partly dependent on the VraSR TCS. Msr contributes to staphylococcal responses to oxidative attack and PMN. Our study highlights a novel interaction between the oxidative protein repair pathway and the VraSR TCS that is involved in cell wall homeostasis.
© 2013 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Significance of four methionine sulfoxide reductases in Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 13;10(2):e0117594. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117594. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25680075 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus Peptide Methionine Sulfoxide Reductases Protect from Human Whole-Blood Killing.Infect Immun. 2021 Jul 15;89(8):e0014621. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00146-21. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Infect Immun. 2021. PMID: 34001560 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple methionine sulfoxide reductase genes in Staphylococcus aureus: expression of activity and roles in tolerance of oxidative stress.Microbiology (Reading). 2003 Oct;149(Pt 10):2739-2747. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26442-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2003. PMID: 14523107
-
New insights into the molecular physiology of sulfoxide reduction in bacteria.Adv Microb Physiol. 2019;75:1-51. doi: 10.1016/bs.ampbs.2019.05.001. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Adv Microb Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31655735 Review.
-
The Role of Methionine Sulfoxide Reductases in Oxidative Stress Tolerance and Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus and Other Bacteria.Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Sep 28;7(10):128. doi: 10.3390/antiox7100128. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30274148 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The DUF59 Containing Protein SufT Is Involved in the Maturation of Iron-Sulfur (FeS) Proteins during Conditions of High FeS Cofactor Demand in Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS Genet. 2016 Aug 12;12(8):e1006233. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006233. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27517714 Free PMC article.
-
How methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus evade neutrophil killing.Curr Opin Hematol. 2015 Jan;22(1):30-5. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000096. Curr Opin Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25394313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epic Immune Battles of History: Neutrophils vs. Staphylococcus aureus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jun 30;7:286. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00286. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28713774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The copBL operon protects Staphylococcus aureus from copper toxicity: CopL is an extracellular membrane-associated copper-binding protein.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 15;294(11):4027-4044. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004723. Epub 2019 Jan 17. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30655293 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Mechanisms of Macrophages and the Immune Evasion Strategies of Staphylococcus aureus.Pathogens. 2015 Nov 27;4(4):826-68. doi: 10.3390/pathogens4040826. Pathogens. 2015. PMID: 26633519 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vogt W. Oxidation of methionyl residues in proteins: tools, targets, and reversal. Free Radic Biol Med. 1995;18:93–105. - PubMed
-
- Singh VK, Moskovitz J, Wilkinson BJ, Jayaswal RK. Molecular characterization of a chromosomal locus in Staphylococcus aureus that contributes to oxidative defence and is highly induced by the cell-wall-active antibiotic oxacillin. Microbiology. 2001;147:3037–3045. - PubMed
-
- Singh VK, Moskovitz J. Multiple methionine sulfoxide reductase genes in Staphylococcus aureus: expression of activity and roles in tolerance of oxidative stress. Microbiology. 2003;149:2739–2747. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

