Transcriptional regulation of T helper type 2 differentiation
- PMID: 24245687
- PMCID: PMC3956424
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12216
Transcriptional regulation of T helper type 2 differentiation
Abstract
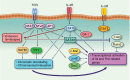
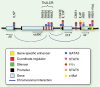
Considerable progress has been made in recent years towards our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of transcriptional regulation of T helper type 2 (Th2) cell differentiation. Additional transcription factors and chromatin-modifying factors were identified and shown to promote Th2 cell differentiation and inhibit differentiation into other subsets. Analyses of mice lacking several cis-regulatory elements have yielded more insight into the regulatory mechanism of Th2 cytokine genes. Gene deletion studies of several chromatin modifiers confirmed their impact on CD4 T-cell differentiation. In addition, recent genome-wide analyses of transcription factor binding and chromatin status revealed unexpected roles of these factors in Th2-cell differentiation. In this review, these recent findings and their implication are summarized.
Keywords: T helper type 2; cis-regulatory element; differentiation; epigenetics; transcription factor.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
'All things considered': transcriptional regulation of T helper type 2 cell differentiation from precursor to effector activation.Immunology. 2013 Sep;140(1):31-8. doi: 10.1111/imm.12121. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23668241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T helper cell differentiation: regulation by cis elements and epigenetics.Immunity. 2006 Apr;24(4):369-79. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.03.007. Immunity. 2006. PMID: 16618596 Review.
-
Chromatin remodeling and T helper subset differentiation.IUBMB Life. 2000 Jun;49(6):473-8. doi: 10.1080/15216540050166990. IUBMB Life. 2000. PMID: 11032239 Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of Th2 cytokine expression in atopic diseases.Tissue Antigens. 2008 Aug;72(2):91-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.2008.01068.x. Epub 2008 Jun 28. Tissue Antigens. 2008. PMID: 18554247 Review.
-
Control of cytokine gene transcription in Th1 and Th2 cells.Clin Exp Allergy. 2008 Sep;38(9):1422-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.03067.x. Epub 2008 Jul 19. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008. PMID: 18647314 Review.
Cited by
-
The RNA-Binding Protein KSRP Modulates Cytokine Expression of CD4+ T Cells.J Immunol Res. 2019 Aug 14;2019:4726532. doi: 10.1155/2019/4726532. eCollection 2019. J Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 31511826 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation and Regulation of Bovine Th2 Cells In Vitro.Cells. 2024 Apr 24;13(9):738. doi: 10.3390/cells13090738. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38727273 Free PMC article.
-
A Mutation in the Transcription Factor Foxp3 Drives T Helper 2 Effector Function in Regulatory T Cells.Immunity. 2019 Feb 19;50(2):362-377.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.12.016. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Immunity. 2019. PMID: 30709738 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of T-bet, GATA-3 and TGF-ß Induces IFN-γ, IL-4/13A, and IL-17A Expression in Atlantic Salmon.Biology (Basel). 2020 Apr 20;9(4):82. doi: 10.3390/biology9040082. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32326041 Free PMC article.
-
The Dysfunctional Immune System in Common Variable Immunodeficiency Increases the Susceptibility to Gastric Cancer.Cells. 2020 Jun 19;9(6):1498. doi: 10.3390/cells9061498. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32575504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou L, Chong MM, Littman DR. Plasticity of CD4+ T cell lineage differentiation. Immunity. 2009;30:646–55. - PubMed
-
- Cousins DJ, Lee TH, Staynov DZ. Cytokine coexpression during human Th1/Th2 cell differentiation: direct evidence for coordinated expression of Th2 cytokines. J Immunol. 2002;169:2498–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

