Cerebral arterial pulsation drives paravascular CSF-interstitial fluid exchange in the murine brain
- PMID: 24227727
- PMCID: PMC3866416
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1592-13.2013
Cerebral arterial pulsation drives paravascular CSF-interstitial fluid exchange in the murine brain
Abstract
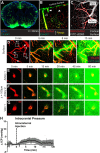
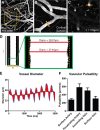
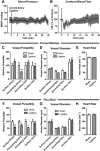
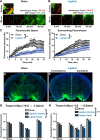
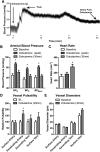
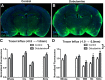
CSF from the subarachnoid space moves rapidly into the brain along paravascular routes surrounding penetrating cerebral arteries, exchanging with brain interstitial fluid (ISF) and facilitating the clearance of interstitial solutes, such as amyloid β, in a pathway that we have termed the "glymphatic" system. Prior reports have suggested that paravascular bulk flow of CSF or ISF may be driven by arterial pulsation. However, cerebral arterial pulsation could not be directly assessed. In the present study, we use in vivo two-photon microscopy in mice to visualize vascular wall pulsatility in penetrating intracortical arteries. We observed that unilateral ligation of the internal carotid artery significantly reduced arterial pulsatility by ~50%, while systemic administration of the adrenergic agonist dobutamine increased pulsatility of penetrating arteries by ~60%. When paravascular CSF-ISF exchange was evaluated in real time using in vivo two-photon and ex vivo fluorescence imaging, we observed that internal carotid artery ligation slowed the rate of paravascular CSF-ISF exchange, while dobutamine increased the rate of paravascular CSF-ISF exchange. These findings demonstrate that cerebral arterial pulsatility is a key driver of paravascular CSF influx into and through the brain parenchyma, and suggest that changes in arterial pulsatility may contribute to accumulation and deposition of toxic solutes, including amyloid β, in the aging brain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impairment of paravascular clearance pathways in the aging brain.Ann Neurol. 2014 Dec;76(6):845-61. doi: 10.1002/ana.24271. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Ann Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25204284 Free PMC article.
-
A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid β.Sci Transl Med. 2012 Aug 15;4(147):147ra111. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003748. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22896675 Free PMC article.
-
Paravascular spaces at the brain surface: Low resistance pathways for cerebrospinal fluid flow.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018 Apr;38(4):719-726. doi: 10.1177/0271678X17737984. Epub 2017 Oct 17. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018. PMID: 29039724 Free PMC article.
-
Paravascular spaces: entry to or exit from the brain?Exp Physiol. 2019 Jul;104(7):1013-1017. doi: 10.1113/EP087424. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Exp Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30582766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Paravascular Pathway for Brain Waste Clearance: Current Understanding, Significance and Controversy.Front Neuroanat. 2017 Nov 7;11:101. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2017.00101. eCollection 2017. Front Neuroanat. 2017. PMID: 29163074 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation increases the brain's drainage efficiency in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021 Jun 2;9(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s40478-021-01198-3. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021. PMID: 34078467 Free PMC article.
-
The glymphatic system and its role in cerebral homeostasis.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020 Dec 1;129(6):1330-1340. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00852.2019. Epub 2020 Oct 1. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020. PMID: 33002383 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothermia reduces glymphatic transportation in traumatic edematous brain assessed by intrathecal dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI.Front Neurol. 2022 Oct 20;13:957055. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.957055. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36341130 Free PMC article.
-
Deep-learning-based segmentation of perivascular spaces on T2-Weighted 3T magnetic resonance images.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Aug 29;16:1457405. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1457405. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39267720 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Body Posture on Brain Glymphatic Transport.J Neurosci. 2015 Aug 5;35(31):11034-44. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1625-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26245965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beach TG, Wilson JR, Sue LI, Newell A, Poston M, Cisneros R, Pandya Y, Esh C, Connor DJ, Sabbagh M, Walker DG, Roher AE. Circle of Willis atherosclerosis: association with Alzheimer's disease, neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;113:13–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
