microRNAs in cancer cell response to ionizing radiation
- PMID: 24206455
- PMCID: PMC4066235
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2013.5718
microRNAs in cancer cell response to ionizing radiation
Abstract
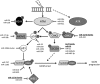
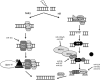
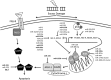
Significance: microRNAs (miRNA) have been characterized as master regulators of the genome. As such, miRNAs are responsible for regulating almost every cellular pathway, including the DNA damage response (DDR) after ionizing radiation (IR). IR is a therapeutic tool that is used for the treatment of several types of cancer, yet the mechanism behind radiation response is not fully understood.
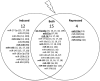
Recent advances: It has been demonstrated that IR can alter miRNA expression profiles, varying greatly from one cell type to the next. It is possible that this variation contributes to the range of tumor cell responsiveness that is observed after radiotherapy, especially considering the extensive role for miRNAs in regulating the DDR. In addition, individual miRNAs or miRNA families have been shown to play a multifaceted role in the DDR, regulating multiple members in a single pathway.
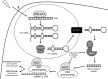
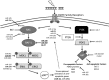
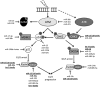
Critical issues: In this review, we will discuss the effects of radiation on miRNA expression as well as explore the function of miRNAs in regulating the cellular response to radiation-induced damage. We will discuss the importance of miRNA regulation at each stage of the DDR, including signal transduction, DNA damage sensing, cell cycle checkpoint activation, DNA double-strand break repair, and apoptosis. We will focus on emphasizing the importance of a single miRNA targeting several mediators within a pathway.
Future directions: miRNAs will continue to emerge as critical regulators of the DDR. Understanding the role of miRNAs in the response to IR will provide insights for improving the current standard therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
microRNA expression and biogenesis in cellular response to ionizing radiation.DNA Cell Biol. 2014 Oct;33(10):667-79. doi: 10.1089/dna.2014.2401. Epub 2014 Jun 6. DNA Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24905898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p53 shapes genome-wide and cell type-specific changes in microRNA expression during the human DNA damage response.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(16):2572-86. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2015.942209. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25486198 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage response regulation by microRNAs as a therapeutic target in cancer.DNA Repair (Amst). 2016 Nov;47:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.09.003. Epub 2016 Sep 27. DNA Repair (Amst). 2016. PMID: 27697364 Review.
-
MicroRNAs: new players in the DNA damage response.J Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jun;3(3):151-8. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjq042. Epub 2010 Dec 23. J Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21183529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs, DNA Damage Response, and Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 12;17(12):2087. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122087. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27973455 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of DNA Damage Response and Homologous Recombination Repair by microRNA in Human Cells Exposed to Ionizing Radiation.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 8;12(7):1838. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071838. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32650508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A radiosensitivity MiRNA signature validated by the TCGA database for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 27;6(33):34649-57. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5299. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26452218 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging biomarkers for the combination of radiotherapy and immune checkpoint blockers.Semin Cancer Biol. 2018 Oct;52(Pt 2):125-134. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.12.007. Epub 2017 Dec 16. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018. PMID: 29258856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revisiting cancer hallmarks: insights from the interplay between oxidative stress and non-coding RNAs.Mol Biomed. 2020 Aug 31;1(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s43556-020-00004-1. Mol Biomed. 2020. PMID: 35006436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiation-inducible miR-770-5p sensitizes tumors to radiation through direct targeting of PDZ-binding kinase.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Mar 23;8(3):e2693. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.116. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28333152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afanasyeva EA, Mestdagh P, Kumps C, Vandesompele J, Ehemann V, Theissen J, Fischer M, Zapatka M, Brors B, Savelyeva L, Sagulenko V, Speleman F, Schwab M, and Westermann F. MicroRNA miR-885-5p targets CDK2 and MCM5, activates p53 and inhibits proliferation and survival. Cell Death Differ 18: 974–984, 2011 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

