A novel antisense RNA from the Salmonella virulence plasmid pSLT expressed by non-growing bacteria inside eukaryotic cells
- PMID: 24205037
- PMCID: PMC3815029
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077939
A novel antisense RNA from the Salmonella virulence plasmid pSLT expressed by non-growing bacteria inside eukaryotic cells
Abstract
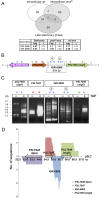
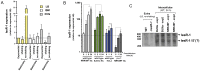
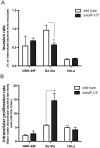
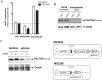
Bacterial small RNAs (sRNAs) are regulatory molecules playing relevant roles in response to environmental changes, stressful conditions and pathogenesis. The intracellular bacterial pathogen Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium) is known to regulate expression of some sRNAs during colonization of fibroblasts. Here, we characterize a previously unknown sRNA encoded in the S. Typhimurium pSLT virulence plasmid that is specifically up-regulated by non-growing dormant bacteria persisting inside fibroblasts. This sRNA was inferred in microarray expression analyses, which unraveled enhanced transcriptional activity in the PSLT047- PSLT046 (mig5) intergenic region. The sRNA transcript was further identified as a 597-nucleotide molecule, which we named IesR-1, for 'Intracellular-expressed-sRNA-1'. IesR-1 expression is low in bacteria growing in axenic cultures across a variety of experimental conditions but displays a marked increase (∼200-300 fold) following bacterial entry into fibroblasts. Remarkably, induction of IesR-1 expression is not prominent in bacteria proliferating within epithelial cells. IesR-1 deletion affects the control of bacterial growth in defined fibroblast cell lines and impairs virulence in a mouse infection model. Expression analyses performed in the PSLT047-iesR-1-PSLT046 (mig5) region support a cis-acting regulatory mechanism of IesR-1 as antisense RNA over the PSLT047 transcript involving interaction at their respective 3' ends and modulation of PSLT047 protein levels. This model is sustained by the scarce production of PSLT047 protein observed in non-growing intracellular bacteria and the high amount of PSLT047 protein produced by bacteria carrying a truncated IesR-1 version with separated 5' and 3' regions. Taken together, these data reveal that S. Typhimurium sRNAs encoded in the pSLT virulence plasmid respond to a state of persistence inside the host cell. As exemplified by IesR-1, some of these sRNAs may contribute to diminish the relative levels of proteins, such as PSLT047, which are probably dispensable for the intracellular lifestyle.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Non-coding RNA regulation in pathogenic bacteria located inside eukaryotic cells.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Nov 12;4:162. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00162. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25429360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of Salmonella small RNA expression in non-growing bacteria located inside eukaryotic cells.RNA Biol. 2012 Apr;9(4):469-88. doi: 10.4161/rna.19317. Epub 2012 Feb 16. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 22336761
-
A Salmonella small non-coding RNA facilitates bacterial invasion and intracellular replication by modulating the expression of virulence factors.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Sep;7(9):e1002120. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002120. Epub 2011 Sep 15. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21949647 Free PMC article.
-
Genome expression analysis of nonproliferating intracellular Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium unravels an acid pH-dependent PhoP-PhoQ response essential for dormancy.Infect Immun. 2013 Jan;81(1):154-65. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01080-12. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 23090959 Free PMC article.
-
The expanding targetome of small RNAs in Salmonella Typhimurium.Biochimie. 2017 Jun;137:69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2017.03.005. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Biochimie. 2017. PMID: 28302471 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA-based mechanisms of virulence control in Enterobacteriaceae.RNA Biol. 2017 May 4;14(5):471-487. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1201617. Epub 2016 Jul 21. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 27442607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNA regulation in pathogenic bacteria located inside eukaryotic cells.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Nov 12;4:162. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00162. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25429360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Small RNA RyhB Homologs from Salmonella Typhimurium Restrain the Intracellular Growth and Modulate the SPI-1 Gene Expression within RAW264.7 Macrophages.Microorganisms. 2021 Mar 18;9(3):635. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9030635. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33803635 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

