Aliskiren attenuates steatohepatitis and increases turnover of hepatic fat in mice fed with a methionine and choline deficient diet
- PMID: 24204981
- PMCID: PMC3804600
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077817
Aliskiren attenuates steatohepatitis and increases turnover of hepatic fat in mice fed with a methionine and choline deficient diet
Abstract
Background & aims: Activation of the renin-angiotensin-system is known to play a role in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Renin knockout mice manifest decreased hepatic steatosis. Aliskiren is the first direct renin inhibitor to be approved for clinical use. Our study aims to evaluate the possible therapeutic effects and mechanism of the chronic administration of aliskiren in a dietary steatohepatitis murine model.
Methods: Male C57BL/6 mice were fed with a methionine and choline-deficient (MCD) diet to induce steatohepatitis. After 8 weeks of feeding, the injured mice were randomly assigned to receive aliskiren (50 mg·kg(-1) per day) or vehicle administration for 4 weeks. Normal controls were also administered aliskiren (50 mg·kg(-1) per day) or a vehicle for 4 weeks.
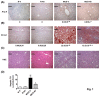
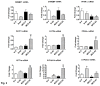
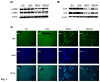
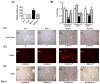
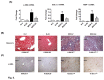
Results: In the MCD mice, aliskiren attenuated hepatic steatosis, inflammation and fibrosis. Aliskiren did not change expression of lipogenic genes but increase turnover of hepatic fat by up-regulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a, cytochrome P450-4A14 and phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase. Furthermore, aliskiren decreased the hepatic expression of angiotensin II and nuclear factor κB. The levels of oxidative stress, hepatocyte apoptosis, activation of Kupffer cells and hepatic stellate cells, and pro-fibrotic markers were also reduced in the livers of the MCD mice receiving aliskiren.
Conclusions: Aliskiren attenuates steatohepatitis and fibrosis in mice fed with a MCD diet. Thus, the noted therapeutic effects might come from not only the reduction of angiotensin II but also the up-regulation of fatty acid oxidation-related genes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sitagliptin attenuates methionine/choline-deficient diet-induced steatohepatitis.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014 Jul;105(1):47-57. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2014.04.028. Epub 2014 May 1. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014. PMID: 24842243
-
Aliskiren Reduces Hepatic steatosis and Epididymal Fat Mass and Increases Skeletal Muscle Insulin Sensitivity in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 6;6:18899. doi: 10.1038/srep18899. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26732252 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of bezafibrate, PPAR pan-agonist, and GW501516, PPARdelta agonist, on development of steatohepatitis in mice fed a methionine- and choline-deficient diet.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Apr 24;536(1-2):182-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.02.028. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16574099
-
Attenuated progression of diet-induced steatohepatitis in glutathione-deficient mice.Lab Invest. 2010 Dec;90(12):1704-17. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.112. Epub 2010 Jun 14. Lab Invest. 2010. PMID: 20548286 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-lipoic acid attenuates methionine choline deficient diet-induced steatohepatitis in C57BL/6 mice.Life Sci. 2012 Jan 30;90(5-6):200-5. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2011.11.012. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22154902
Cited by
-
Hepatoprotective and Anti-fibrotic Agents: It's Time to Take the Next Step.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Jan 7;6:303. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00303. eCollection 2015. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26779021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-diabetic and renoprotective effects of aliskiren in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in female rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016 Dec;389(12):1315-1324. doi: 10.1007/s00210-016-1299-2. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27612855
-
Aliskiren Attenuates the Inflammatory Response and Wound Healing Process in Diabetic Mice With Periodontal Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 4;10:708. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00708. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31333451 Free PMC article.
-
TGR(mREN2)27 rats develop non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-associated portal hypertension responsive to modulations of Janus-kinase 2 and Mas receptor.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 12;9(1):11598. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48024-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31406138 Free PMC article.
-
Si-Wei-Qing-Gan-Tang Improves Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Modulating the Nuclear Factor-κB Signal Pathway and Autophagy in Methionine and Choline Deficient Diet-Fed Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2020 May 1;11:530. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00530. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32425782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Diehl AM, Brunt EM et al. (2012) The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology 55: 2005-2023. doi:10.1002/hep.25762. PubMed: 22488764. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jayasooriya AP, Mathai ML, Walker LL, Begg DP, Denton DA et al. (2008) Mice lacking angiotensin-converting enzyme have increased energy expenditure, with reduced fat mass and improved glucose clearance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105: 6531-6536. doi:10.1073/pnas.0802690105. PubMed: 18443281. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

