Update and critical appraisal of sevelamer in the management of chronic renal failure
- PMID: 24198624
- PMCID: PMC3818887
- DOI: 10.2147/OAJU.S7227
Update and critical appraisal of sevelamer in the management of chronic renal failure
Abstract
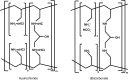
Sevelamer (Renagel and Renvela), is an orally administered weakly basic anion exchange resin that binds dietary phosphate in the gastrointestinal tract, and is approved for use in the US, Europe and many other countries for the treatment of hyperphosphatemia in adult patients on hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Clinical evidence shows that sevelamer is at least as effective as calcium-based oral phosphate binders in controlling serum phosphate, but with a lower incidence of hypercalcemia. Whilst sevelamer hydrochloride is associated with mild acidosis, sevelamer carbonate does not have this drawback. Use of sevelamer and avoidance of calcium-based binders may slow the progression of vascular calcification in hemodialysis patients, and it also reduces serum low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels. There was no between-group difference in all-cause mortality between sevelamer and calcium-based phosphate binder therapy in the primary efficacy analysis of the large (n >2100), 3-year DCOR trial. In the smaller (n = 109) nonblind RIND trial in patients new to hemodialysis, data suggest there may be an overall survival benefit with sevelamer versus calcium-based phosphate binder treatment but the evidence on the efficacy of sevelamer in reducing mortality and hospitalization is not strong. The balance of evidence, however, does not strongly support the use of sevelamer over the much less costly calcium-based binders except in patients at risk of hypercalcemic episodes. Further research into cardiovascular and all-cause mortality over a longer time period would be needed to settle this issue, and the relative survival benefits and cost effectiveness of all phosphate binder therapies remains to be fully determined. Despite the relative paucity of data available, sevelamer has established itself as the most widely used binder in the United States and the most widely used noncalcium-based binder worldwide. However, affordability is a major issue for most health economies and in the light of recent economic events is likely to become more prominent.
Keywords: binder; dialysis; phosphate; phosphorus; sevelamer; vascular calcification.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sevelamer hydrochloride: a review of its use for hyperphosphataemia in patients with end-stage renal disease on haemodialysis.Drugs. 2008;68(1):85-104. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200868010-00006. Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18081374 Review.
-
Phosphate binders: Sevelamer in the prevention and treatment of hyperphosphataemia in chronic renal failure.Hippokratia. 2011 Jan;15(Suppl 1):22-6. Hippokratia. 2011. PMID: 21897754 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of morbidity and mortality data related to cardiovascular calcification from calcium-containing phosphate binder use in patients undergoing hemodialysis.Pharmacotherapy. 2010 Jul;30(7):741-8. doi: 10.1592/phco.30.7.741. Pharmacotherapy. 2010. PMID: 20575637 Review.
-
Calcium salts in the treatment of hyperphosphatemia in hemodialysis patients.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2003 Jul;12(4):373-9. doi: 10.1097/00041552-200307000-00005. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2003. PMID: 12815333 Review.
-
The effect of sevelamer hydrochloride and calcium-based phosphate binders on mortality in hemodialysis patients: a need for more research.Consult Pharm. 2010 Jan;25(1):41-54. doi: 10.4140/TCP.n.2010.41. Consult Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20211816 Review.
Cited by
-
Sevelamer Carbonate Crystal-Induced Colitis.Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2020 Jul 23;2020:4646732. doi: 10.1155/2020/4646732. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2020. PMID: 32774946 Free PMC article.
-
Sevelamer-Associated Rectosigmoid Ulcers in an End-Stage Renal Disease Patient.ACG Case Rep J. 2018 Nov 28;5:e83. doi: 10.14309/crj.2018.83. eCollection 2018. ACG Case Rep J. 2018. PMID: 30568971 Free PMC article.
-
Colonic Ulcerations in a Patient on Hemodialysis.Indian J Nephrol. 2018 Jul-Aug;28(4):329-330. doi: 10.4103/ijn.IJN_172_17. Indian J Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30158758 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Colonic Mass Secondary to Sevelamer-Associated Mucosal Injury.ACG Case Rep J. 2017 Aug 2;4:e92. doi: 10.14309/crj.2017.92. eCollection 2017. ACG Case Rep J. 2017. PMID: 28798940 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Preclinical studies of VS-505: a non-absorbable highly effective phosphate binder.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Jul;173(14):2278-89. doi: 10.1111/bph.13510. Epub 2016 Jun 12. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27156057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martin KJ, Gonzalez EA. Metabolic bone disease in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:875–885. - PubMed
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD-MBD Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD) Kidney Int Suppl. 2009;(113):S1–S130. - PubMed
-
- Moe S, Drueke T, Cunningham J, et al. Definition, evaluation, and classification of renal osteodystrophy: a position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Kidney Int. 2006;69:1945–1953. - PubMed
-
- Floege J, Ketteler M. Vascular calcification in patients with end-stage renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19(Suppl 5):V59–V66. - PubMed
-
- London GM, Pannier B, Guerin AP, Marchais SJ, Safar ME, Cuche JL. Cardiac hypertrophy, aortic compliance, peripheral resistance, and wave reflection in end-stage renal disease. Comparative effects of ACE inhibition and calcium channel blockade. Circulation. 1994;90:2786–2796. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

