Advances in Rosetta structure prediction for difficult molecular-replacement problems
- PMID: 24189231
- PMCID: PMC3817693
- DOI: 10.1107/S0907444913023305
Advances in Rosetta structure prediction for difficult molecular-replacement problems
Abstract
Recent work has shown the effectiveness of structure-prediction methods in solving difficult molecular-replacement problems. The Rosetta protein structure modeling suite can aid in the solution of difficult molecular-replacement problems using templates from 15 to 25% sequence identity; Rosetta refinement guided by noisy density has consistently led to solved structures where other methods fail. In this paper, an overview of the use of Rosetta for these difficult molecular-replacement problems is provided and new modeling developments that further improve model quality are described. Several variations to the method are introduced that significantly reduce the time needed to generate a model and the sampling required to improve the starting template. The improvements are benchmarked on a set of nine difficult cases and it is shown that this improved method obtains consistently better models in less running time. Finally, strategies for best using Rosetta to solve difficult molecular-replacement problems are presented and future directions for the role of structure-prediction methods in crystallography are discussed.
Keywords: model building; molecular replacement; structure prediction.
Figures

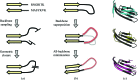
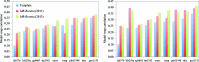

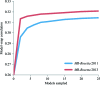
Similar articles
-
Rosetta Structure Prediction as a Tool for Solving Difficult Molecular Replacement Problems.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1607:455-466. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7000-1_19. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28573585 Review.
-
Structure prediction for CASP8 with all-atom refinement using Rosetta.Proteins. 2009;77 Suppl 9(0 9):89-99. doi: 10.1002/prot.22540. Proteins. 2009. PMID: 19701941 Free PMC article.
-
phenix.mr_rosetta: molecular replacement and model rebuilding with Phenix and Rosetta.J Struct Funct Genomics. 2012 Jun;13(2):81-90. doi: 10.1007/s10969-012-9129-3. Epub 2012 Mar 15. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22418934 Free PMC article.
-
SCEDS: protein fragments for molecular replacement in Phaser.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 Nov;69(Pt 11):2216-25. doi: 10.1107/S0907444913021811. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013. PMID: 24189233 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular replacement: tricks and treats.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 Nov;69(Pt 11):2167-73. doi: 10.1107/S0907444913015291. Epub 2013 Oct 12. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013. PMID: 24189227 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The second messenger c-di-AMP inhibits the osmolyte uptake system OpuC in Staphylococcus aureus.Sci Signal. 2016 Aug 16;9(441):ra81. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaf7279. Sci Signal. 2016. PMID: 27531650 Free PMC article.
-
DNA backbone interactions impact the sequence specificity of DNA sulfur-binding domains: revelations from structural analyses.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Sep 4;48(15):8755-8766. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa574. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32621606 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for autophagy inhibition by the human Rubicon-Rab7 complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jul 21;117(29):17003-17010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2008030117. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32632011 Free PMC article.
-
X-ray structure and activities of an essential Mononegavirales L-protein domain.Nat Commun. 2015 Nov 9;6:8749. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9749. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26549102 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of AlphaFold2 for crystallographic phasing by molecular replacement.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2022 Jan 1;78(Pt 1):1-13. doi: 10.1107/S2059798321012122. Epub 2022 Jan 1. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2022. PMID: 34981757 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

