Bluetongue virus infection induces aberrant mitosis in mammalian cells
- PMID: 24165208
- PMCID: PMC3874736
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-319
Bluetongue virus infection induces aberrant mitosis in mammalian cells
Abstract
Background: Bluetongue virus (BTV) is an arbovirus that is responsible for 'bluetongue', an economically important disease of livestock. Although BTV is well characterised at the protein level, less is known regarding its interaction with host cells. During studies of virus inclusion body formation we observed what appeared to be a large proportion of cells in mitosis. Although the modulation of the cell cycle is well established for many viruses, this was a novel observation for BTV. We therefore undertook a study to reveal in more depth the impact of BTV upon cell division.
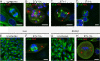
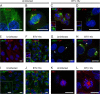
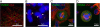
Methods: We used a confocal microscopy approach to investigate the localisation of BTV proteins in a cellular context with their respective position relative to cellular proteins. In addition, to quantitatively assess the frequency of aberrant mitosis induction by the viral non-structural protein (NS) 2 we utilised live cell imaging to monitor HeLa-mCherry tubulin cells transfected with a plasmid expressing NS2.
Results: Our data showed that these 'aberrant mitoses' can be induced in multiple cell types and by different strains of BTV. Further study confirmed multiplication of the centrosomes, each resulting in a separate mitotic spindle during mitosis. Interestingly, the BTV NS1 protein was strongly localised to the centrosomal regions. In a separate, yet related observation, the BTV NS2 protein was co-localised with the condensed chromosomes to a region suggestive of the kinetochore. Live cell imaging revealed that expression of an EGFP-NS2 fusion protein in HeLa-mCherry tubulin cells also results in mitotic defects.
Conclusions: We hypothesise that NS2 is a microtubule cargo protein that may inadvertently disrupt the interaction of microtubule tips with the kinetochores during mitosis. Furthermore, the BTV NS1 protein was distinctly localised to a region encompassing the centrosome and may therefore be, at least in part, responsible for the disruption of the centrosome as observed in BTV infected mammalian cells.
Figures
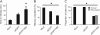
Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of a novel non-structural protein of bluetongue virus.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Dec;7(12):e1002477. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002477. Epub 2011 Dec 29. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 22241985 Free PMC article.
-
Bluetongue virus RNA binding protein NS2 is a modulator of viral replication and assembly.BMC Mol Biol. 2007 Jan 22;8:4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-4. BMC Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17241458 Free PMC article.
-
A Calcium Sensor Discovered in Bluetongue Virus Nonstructural Protein 2 Is Critical for Virus Replication.J Virol. 2020 Sep 29;94(20):e01099-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01099-20. Print 2020 Sep 29. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32759321 Free PMC article.
-
A review of experimental infections with bluetongue virus in the mammalian host.Virus Res. 2014 Mar;182:21-34. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2013.12.044. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Virus Res. 2014. PMID: 24462840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the role of the non-structural protein 2 (NS2) in Bluetongue virus morphogenesis.Virus Res. 2010 Aug;151(2):109-17. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.05.014. Virus Res. 2010. PMID: 20621672 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the Role of African Horse Sickness Virus VP7 Protein Crystalline Particles on Virus Replication and Release.Viruses. 2022 Oct 4;14(10):2193. doi: 10.3390/v14102193. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36298748 Free PMC article.
-
Confocal Microscopy of Fluorescently Labeled EHDV-Infected Cell Cultures.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2838:91-100. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4035-7_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39126625
-
In Vitro Reassortment between Endemic Bluetongue Viruses Features Global Shifts in Segment Frequencies and Preferred Segment Combinations.Microorganisms. 2021 Feb 16;9(2):405. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9020405. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33669284 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoproteomic Analysis Reveals the Importance of Kinase Regulation During Orbivirus Infection.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017 Nov;16(11):1990-2005. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M117.067355. Epub 2017 Aug 29. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28851738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wade-Evans AM, Mertens PP, Belsham GJ. Sequence of genome segment 9 of bluetongue virus (serotype 1, South Africa) and expression analysis demonstrating that different forms of VP6 are derived from initiation of protein synthesis at two distinct sites. J Gen Virol. 1992;10(Pt 11):3023–3026. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

