Aminobisphosphonates prevent the inhibitory effects exerted by lymph node stromal cells on anti-tumor Vδ 2 T lymphocytes in non-Hodgkin lymphomas
- PMID: 24162786
- PMCID: PMC4007944
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2013.097311
Aminobisphosphonates prevent the inhibitory effects exerted by lymph node stromal cells on anti-tumor Vδ 2 T lymphocytes in non-Hodgkin lymphomas
Abstract
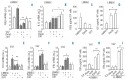
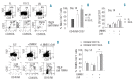
In this study, we analyzed the influence of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from lymph nodes of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, on effector functions and differentiation of Vdelta (δ)2 T lymphocytes. We show that: i) lymph-node mesenchymal stromal cells of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma inhibit NKG2D-mediated lymphoid cell killing, but not rituximab-induced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, exerted by Vδ2 T lymphocytes; ii) pre-treatment of mesenchymal stromal cells with the aminobisphosphonates pamidronate or zoledronate can rescue lymphoma cell killing via NKG2D; iii) this is due to inhibition of transforming growth factor-β and increase in interleukin-15 production by mesenchymal stromal cells; iv) aminobisphosphonate-treated mesenchymal stromal cells drive Vδ2 T-lymphocyte differentiation into effector memory T cells, expressing the Thelper1 cytokines tumor necrosis factor-α and interferon-γ. In non-Hodgkin's lymphoma lymph nodes, Vδ2 T cells were mostly naïve; upon co-culture with autologous lymph-node mesenchymal stromal cells exposed to zoledronate, the percentage of terminal differentiated effector memory Vδ2 T lymphocytes increased. In all non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, low or undetectable transcription of Thelper1 cytokines was found. In diffused large B-cell lymphomas and in a group of follicular lymphoma, transcription of transforming growth factor β and interleukin-10 was enhanced compared to non-neoplastic lymph nodes. Thus, in non-Hodgkin lymphomas mesenchymal stromal cells interfere with Vδ2 T-lymphocyte cytolytic function and differentiation to Thelper1 and/or effector memory cells, depending on the prominent in situ cytokine milieu. Aminobisphosphonates, acting on lymph-node mesenchymal stromal cells, can push the balance towards Thelper1/effector memory and rescue the recognition and killing of lymphoma cells through NKG2D, sparing rituximab-induced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
High ERp5/ADAM10 expression in lymph node microenvironment and impaired NKG2D ligands recognition in Hodgkin lymphomas.Blood. 2012 Feb 9;119(6):1479-89. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-07-370841. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22167753
-
Differentiation of antitumor-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes from autologous tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.Exp Hematol. 1999 Jul;27(7):1185-93. doi: 10.1016/s0301-472x(99)00057-0. Exp Hematol. 1999. PMID: 10390194
-
Distribution of lymphocytes with interleukin-2 receptors (TAC antigens) in reactive lymphoproliferative processes, Hodgkin's disease, and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. An immunohistologic study of 300 cases.Am J Pathol. 1987 Apr;127(1):27-37. Am J Pathol. 1987. PMID: 3105322 Free PMC article.
-
Stress immunity in lymphomas: mesenchymal cells as a target of therapy.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014 Jan 1;19(2):281-90. doi: 10.2741/4207. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014. PMID: 24389184 Review.
-
[Biology and differentiation of lymphocytes in the classification of lymphomas].Recenti Prog Med. 1990 Oct;81(10):621-8. Recenti Prog Med. 1990. PMID: 2291005 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
How to Hit Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Make the Tumor Microenvironment Immunostimulant Rather Than Immunosuppressive.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 19;9:262. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00262. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29515580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reprogramming the tumor microenvironment to improve the efficacy of cancer immunotherapies.Med Oncol. 2022 Sep 29;39(12):239. doi: 10.1007/s12032-022-01842-5. Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36175691 Review.
-
Catch me if you can: how AML and its niche escape immunotherapy.Leukemia. 2022 Jan;36(1):13-22. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01350-x. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Leukemia. 2022. PMID: 34302116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
γδ T cells in immunotherapies for B-cell malignancies.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 22;14:1200003. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1200003. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37426670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells and mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxia and normoxia.Oncol Lett. 2020 Nov;20(5):229. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12092. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32968451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayday AC. Gammadelta T cells and the lymphoid stress-surveillance response. Immunity. 2009;31(2):184–96 - PubMed
-
- Bonneville M, O’Brien RL, Born WK. Gammadelta T cell effector functions: a blend of innate programming and acquired plasticity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(7):467–78 - PubMed
-
- Das H, Wang L, Kamath A, Bukowski JF.V 9V 2 T-cell receptor-mediated recognition of aminobisphosphonates. Blood. 2001;98(5):1616–8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

