A screen for hydroxymethylcytosine and formylcytosine binding proteins suggests functions in transcription and chromatin regulation
- PMID: 24156278
- PMCID: PMC4014808
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-10-r119
A screen for hydroxymethylcytosine and formylcytosine binding proteins suggests functions in transcription and chromatin regulation
Abstract
Background: DNA methylation (5mC) plays important roles in epigenetic regulation of genome function. Recently, TET hydroxylases have been found to oxidise 5mC to hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), formylcytosine (5fC) and carboxylcytosine (5caC) in DNA. These derivatives have a role in demethylation of DNA but in addition may have epigenetic signaling functions in their own right. A recent study identified proteins which showed preferential binding to 5-methylcytosine (5mC) and its oxidised forms, where readers for 5mC and 5hmC showed little overlap, and proteins bound to further oxidation forms were enriched for repair proteins and transcription regulators. We extend this study by using promoter sequences as baits and compare protein binding patterns to unmodified or modified cytosine using DNA from mouse embryonic stem cell extracts.
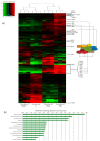
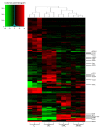
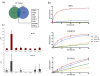
Results: We compared protein enrichments from two DNA probes with different CpG composition and show that, whereas some of the enriched proteins show specificity to cytosine modifications, others are selective for both modification and target sequences. Only a few proteins were identified with a preference for 5hmC (such as RPL26, PRP8 and the DNA mismatch repair protein MHS6), but proteins with a strong preference for 5fC were more numerous, including transcriptional regulators (FOXK1, FOXK2, FOXP1, FOXP4 and FOXI3), DNA repair factors (TDG and MPG) and chromatin regulators (EHMT1, L3MBTL2 and all components of the NuRD complex).
Conclusions: Our screen has identified novel proteins that bind to 5fC in genomic sequences with different CpG composition and suggests they regulate transcription and chromatin, hence opening up functional investigations of 5fC readers.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide distribution of 5-formylcytosine in embryonic stem cells is associated with transcription and depends on thymine DNA glycosylase.Genome Biol. 2012 Aug 17;13(8):R69. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-8-r69. Genome Biol. 2012. PMID: 22902005 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide profiling of 5-formylcytosine reveals its roles in epigenetic priming.Cell. 2013 Apr 25;153(3):678-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23602153 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modifications in DNA could mimic oxidative DNA damage: A double-edged sword.DNA Repair (Amst). 2015 Aug;32:52-57. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.04.013. Epub 2015 May 1. DNA Repair (Amst). 2015. PMID: 25956859 Review.
-
Dysregulation and prognostic potential of 5-methylcytosine (5mC), 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5fC), and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC) levels in prostate cancer.Clin Epigenetics. 2018 Aug 7;10(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13148-018-0540-x. Clin Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 30086793 Free PMC article.
-
[Oxidation and deamination of nucleobases as an epigenetic tool].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012 May 24;66:275-86. doi: 10.5604/17322693.997954. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012. PMID: 22706113 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
X-ray irradiation induces subtle changes in the genome-wide distribution of DNA hydroxymethylation with opposing trends in genic and intergenic regions.Epigenetics. 2019 Jan;14(1):81-93. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2019.1568807. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 30691379 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine during pronuclear development in equine zygotes produced by ICSI.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2017 Mar 15;10:13. doi: 10.1186/s13072-017-0120-x. eCollection 2017. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2017. PMID: 28331549 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Research of Adult Gliomas.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 18;22(2):924. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020924. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33477674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An all-to-all approach to the identification of sequence-specific readers for epigenetic DNA modifications on cytosine.Nat Commun. 2021 Feb 4;12(1):795. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-20950-w. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33542217 Free PMC article.
-
5-Formylcytosine landscapes of human preimplantation embryos at single-cell resolution.PLoS Biol. 2020 Jul 30;18(7):e3000799. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000799. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2020. PMID: 32730243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khare T, Pai S, Koncevicius K, Pal M, Kriukiene E, Liutkeviciute Z, Irimia M, Jia PX, Ptak C, Xia MH, Tice R, Tochigi M, Morera S, Nazarians A, Belsham D, Wong AHC, Blencowe BJ, Wang SC, Kapranov P, Kustra R, Labrie V, Klimasauskas S, Petronis A. 5-hmC in the brain is abundant in synaptic genes and shows differences at the exon-intron boundary. Nat Struct Mole Biol. 2012;14:1037–U1094. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2372. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

