Interleukin-8 regulates endothelial permeability by down-regulation of tight junction but not dependent on integrins induced focal adhesions
- PMID: 24155670
- PMCID: PMC3805902
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.6996
Interleukin-8 regulates endothelial permeability by down-regulation of tight junction but not dependent on integrins induced focal adhesions
Abstract
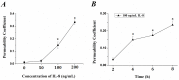
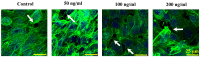
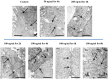
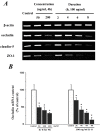
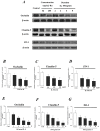
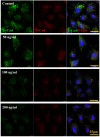
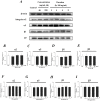
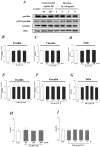
Interleukin-8 (IL-8) is a common inflammatory factor, which involves in various non-specific pathological processes of inflammation. It has been found that increased endothelial permeability accompanied with high expression of IL-8 at site of injured endothelium and atherosclerotic plaque at early stages, suggesting that IL-8 participated in regulating endothelial permeability in the developing processes of vascular disease. The purpose of this study is to investigate the regulation effects of IL-8 on the vascular endothelial permeability, and the mRNA and protein expression of tight junction components (i.e., ZO-1, Claudin-5 and Occludin). Endothelial cells were stimulated by IL-8 with the dose of 50, 100 and 200 ng/mL, and duration of 2, 4, 6, 8h, respectively. The mRNA and protein expression level of tight junction components with IL-8 under different concentration and duration was examined by RT-PCR and Western blot, respectively. Meanwhile, the integrins induced focal adhesions event with IL-8 stimulation was also investigated. The results showed that IL-8 regulated the permeability of endothelium by down-regulation of tight junction in a dose- and time-dependence manner, but was not by integrins induced focal adhesions. This finding reveals the molecular mechanism in the increase of endothelial cell permeability induced by IL-8, which is expected to provide a new idea as a therapeutic target in vascular diseases.
Keywords: Claudin-5; Endothelial permeability; IL-8; Occludin; Tight junction; ZO-1..
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MiR-18a increased the permeability of BTB via RUNX1 mediated down-regulation of ZO-1, occludin and claudin-5.Cell Signal. 2015 Jan;27(1):156-67. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.10.008. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Cell Signal. 2015. PMID: 25452107
-
Plant-derived triterpene celastrol ameliorates oxygen glucose deprivation-induced disruption of endothelial barrier assembly via inducing tight junction proteins.Phytomedicine. 2016 Dec 1;23(13):1621-1628. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.10.006. Epub 2016 Oct 15. Phytomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27823626
-
RhoA/ROCK-2 Pathway Inhibition and Tight Junction Protein Upregulation by Catalpol Suppresses Lipopolysaccaride-Induced Disruption of Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability.Molecules. 2018 Sep 17;23(9):2371. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092371. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30227623 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Regulation of Endothelial Junction Proteins and Clinical Consequence.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:5078627. doi: 10.1155/2016/5078627. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27999452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Krüppel-like factor 4 regulates blood-tumor barrier permeability via ZO-1, occludin and claudin-5.J Cell Physiol. 2014 Jul;229(7):916-26. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24523. J Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24318462
Cited by
-
Optimal Humanized Scg3-Neutralizing Antibodies for Anti-Angiogenic Therapy of Diabetic Retinopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 1;25(17):9507. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179507. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273454 Free PMC article.
-
Dengue Virus Nonstructural Protein 1 Induces Vascular Leakage through Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor and Autophagy.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Jul 13;10(7):e0004828. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004828. eCollection 2016 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 27409803 Free PMC article.
-
Special Focus on the Cellular Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Several Micro-Immunotherapy Formulations: Considerations Regarding Intestinal-, Immune-Axis-Related- and Neuronal-Inflammation Contexts.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Dec 13;15:6695-6717. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S389614. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36536643 Free PMC article.
-
Rickettsia massiliae and Rickettsia conorii Israeli Spotted Fever Strain Differentially Regulate Endothelial Cell Responses.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 22;10(9):e0138830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138830. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26394396 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin facilitates West Nile virus neuroinvasion via neutrophil "Trojan horse" transport.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 5;7(1):4722. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04839-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28680095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mehta D, Malik AB. Signaling mechanisms regulating endothelial permeability. Physiol Rev. 2006;86:279–367. - PubMed
-
- Siflinger-Birnboim A, Johnson A. Protein kinase C modulates pulmonary endothelial permeability: a paradigm for acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003;284:L435–451. - PubMed
-
- Basu S, Sarkar C, Chakroborty D, Nagy J, Mitra RB, Dasgupta PS, Mukhopadhyay D. Ablation of peripheral dopaminergic nerves stimulates malignant tumor growth by inducing vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004;64:5551–5555. - PubMed
-
- Jeliazkova-Mecheva VV, Hymer WC, Nicholas NC, Bobilya DJ. Brief heat shock affects the permeability and thermotolerance of an in vitro blood-brain barrier model of porcine brain microvascular endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 2006;71:108–114. - PubMed
-
- Pickkers P, Sprong T, Eijk L, Hoeven H, Smits P, Deuren M. Vascular endothelial growth factor is increased during the first 48 hours of human septic shock and correlates with vascular permeability. Shock. 2005;24:508–512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

