Enhanced XAO: the ontology of Xenopus anatomy and development underpins more accurate annotation of gene expression and queries on Xenbase
- PMID: 24139024
- PMCID: PMC3816597
- DOI: 10.1186/2041-1480-4-31
Enhanced XAO: the ontology of Xenopus anatomy and development underpins more accurate annotation of gene expression and queries on Xenbase
Abstract
Background: The African clawed frogs Xenopus laevis and Xenopus tropicalis are prominent animal model organisms. Xenopus research contributes to the understanding of genetic, developmental and molecular mechanisms underlying human disease. The Xenopus Anatomy Ontology (XAO) reflects the anatomy and embryological development of Xenopus. The XAO provides consistent terminology that can be applied to anatomical feature descriptions along with a set of relationships that indicate how each anatomical entity is related to others in the embryo, tadpole, or adult frog. The XAO is integral to the functionality of Xenbase (http://www.xenbase.org), the Xenopus model organism database.
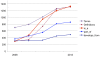
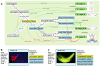
Results: We significantly expanded the XAO in the last five years by adding 612 anatomical terms, 2934 relationships between them, 640 synonyms, and 547 ontology cross-references. Each term now has a definition, so database users and curators can be certain they are selecting the correct term when specifying an anatomical entity. With developmental timing information now asserted for every anatomical term, the ontology provides internal checks that ensure high-quality gene expression and phenotype data annotation. The XAO, now with 1313 defined anatomical and developmental stage terms, has been integrated with Xenbase expression and anatomy term searches and it enables links between various data types including images, clones, and publications. Improvements to the XAO structure and anatomical definitions have also enhanced cross-references to anatomy ontologies of other model organisms and humans, providing a bridge between Xenopus data and other vertebrates. The ontology is free and open to all users.
Conclusions: The expanded and improved XAO allows enhanced capture of Xenopus research data and aids mechanisms for performing complex retrieval and analysis of gene expression, phenotypes, and antibodies through text-matching and manual curation. Its comprehensive references to ontologies across taxa help integrate these data for human disease modeling.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Navigating Xenbase: An Integrated Xenopus Genomics and Gene Expression Database.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1757:251-305. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7737-6_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29761462 Free PMC article.
-
An ontology for Xenopus anatomy and development.BMC Dev Biol. 2008 Sep 25;8:92. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-8-92. BMC Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18817563 Free PMC article.
-
Xenbase: expansion and updates of the Xenopus model organism database.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan;41(Database issue):D865-70. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1025. Epub 2012 Nov 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23125366 Free PMC article.
-
Xenbase: Facilitating the Use of Xenopus to Model Human Disease.Front Physiol. 2019 Feb 26;10:154. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00154. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30863320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward an unbiased evolutionary platform for unraveling Xenopus developmental gene networks.Genesis. 2012 Mar;50(3):186-91. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20811. Epub 2012 Jan 5. Genesis. 2012. PMID: 21956895 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The gene expression database for mouse development (GXD): putting developmental expression information at your fingertips.Dev Dyn. 2014 Oct;243(10):1176-86. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24155. Epub 2014 Jul 4. Dev Dyn. 2014. PMID: 24958384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flow sensing in developing Xenopus laevis is disrupted by visual cues and ototoxin exposure.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2015 Feb;201(2):215-33. doi: 10.1007/s00359-014-0957-4. Epub 2014 Nov 8. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25380559
-
Xenbase, the Xenopus model organism database; new virtualized system, data types and genomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(Database issue):D756-63. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku956. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25313157 Free PMC article.
-
Bio-SimVerb and Bio-SimLex: wide-coverage evaluation sets of word similarity in biomedicine.BMC Bioinformatics. 2018 Feb 5;19(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2039-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29402212 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating Xenbase: An Integrated Xenopus Genomics and Gene Expression Database.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1757:251-305. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7737-6_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29761462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bles EJ. On the breeding habits of Xenopus laevis Daud. Proc Camb Phil Soc. 1901;11:220–222.
-
- Hellsten U, Harland RM, Gilchrist MJ, Hendrix D, Jurka J, Kapitonov V, Ovcharenko I, Putnam NH, Shu S, Taher L, Blitz IL, Blumberg B, Dichmann DS, Dubchak I, Amaya E, Detter JC, Fletcher R, Gerhard DS, Goodstein D, Graves T, Grigoriev IV, Grimwood J, Kawashima T, Lindquist E, Lucas SM, Mead PE, Mitros T, Ogino H, Ohta Y, Poliakov AV, Pollet N, Robert J, Salamov A, Sater AK, Schmutz J, Terry A, Vize PD, Warren WC, Wells D, Wills A, Wilson RK, Zimmerman LB, Zorn AM, Grainger R, Grammer T, Khokha MK, Richardson PM, Rokhsar DS. The genome of the Western clawed frog Xenopus tropicalis. Science. 2010;328(5978):633–636. doi: 10.1126/science.1183670. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xenopus Genome Project. http://polaris.icmb.utexas.edu/index.php/Xenopus_Genome_Project.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

