Tissue factor-targeted lidamycin inhibits growth and metastasis of colon carcinoma
- PMID: 24137414
- PMCID: PMC3789075
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2013.1437
Tissue factor-targeted lidamycin inhibits growth and metastasis of colon carcinoma
Abstract
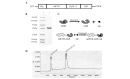
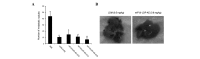
Colon cancer is the third most common cancer in the world. The overexpression of tissue factor (TF) in colon cancer cells makes it an ideal target for colon cancer therapy. The purpose of the present study was to develop a TF-targeting energized fusion protein, mlFVII-LDP-AE, which is composed of a mouse Factor VII light chain (mlFVII) as the targeting domain conjugated to the highly cytotoxic antibiotic lidamycin (LDM, LDP-AE) as the effector domain. The potential efficacy of mlFVII-LDP-AE for mouse colon cancer therapy was tested in a mouse colon cancer subcutaneous xenograft model and a live metastasis model in BALB/c mice. mlFVII-LDP-AE showed a tumor growth inhibition rate of 91.2% (at a dose of 0.8 mg/kg) and a tumor metastasis inhibition rate of 84.7% (at a dose of 0.6 mg/kg). The results showed that mlFVII-LDP-AE was able to effectively inhibit the growth and metastasis of mouse colon cancer. As human TF and FVII have features similar to those of mice, human FVII light chain (hlFVII)-targeted LDM (hlFVII-LDP-AE) may be expected to have therapeutic potential for human colon cancer.
Keywords: colon carcinoma; factor VII; lidamycin; metastasis; tissue factor.
Figures
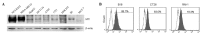
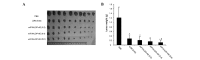
Similar articles
-
Factor VII light chain-targeted lidamycin shows intensified therapeutic efficacy for liver cancer.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2012 Aug;27(6):384-91. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2012.1209. Epub 2012 May 31. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2012. PMID: 22651685 Free PMC article.
-
Factor VII light chain-targeted lidamycin targets tissue factor-overexpressing tumor cells for cancer therapy.Int J Mol Med. 2012 Mar;29(3):409-15. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2011.848. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Int J Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22108624
-
Genetically engineered endostatin-lidamycin fusion proteins effectively inhibit tumor growth and metastasis.BMC Cancer. 2013 Oct 15;13:479. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-479. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24128285 Free PMC article.
-
Tuftsin-based, EGFR-targeting fusion protein and its enediyne-energized analog show high antitumor efficacy associated with CD47 down-regulation.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014 Dec;63(12):1261-72. doi: 10.1007/s00262-014-1604-1. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25164878 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer phenotypes regulated by tissue factor-factor VII pathway: Possible therapeutic targets.World J Clin Oncol. 2014 Dec 10;5(5):908-20. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.908. World J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25493229 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T Cells inhibit the growth and metastases of established tissue factor-positive tumors in NOG mice.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 7;8(6):9488-9499. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14367. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28055955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hong SW, Jung KH, Choi MJ, et al. Anticancer effects of KI-10F: a novel compound affecting apoptosis, angiogenesis and cell growth in colon cancer. Int J Oncol. 2012;41:1715–1722. - PubMed
-
- Amsterdam A, Raanan C, Schreiber L, Freyhan O, Fabrikant Y, Melzer E. Use of multiple biomarkers for the localization and characterization of colon cancer stem cells by indirect immunocytochemistry. Int J Oncol. 2012;41:285–291. - PubMed
-
- Rak J, Milsom C, Magnus N, Yu J. Tissue factor in tumour progression. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2009;22:71–83. - PubMed
-
- Waxman E, Ross JB, Laue TM, et al. Tissue factor and its extracellular soluble domain: the relationship between intermolecular association with factor VIIa and enzymatic activity of the complex. Biochemistry. 1992;31:3998–4003. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
