Genomically recoded organisms expand biological functions
- PMID: 24136966
- PMCID: PMC4924538
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1241459
Genomically recoded organisms expand biological functions
Abstract
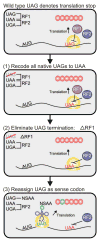
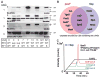
We describe the construction and characterization of a genomically recoded organism (GRO). We replaced all known UAG stop codons in Escherichia coli MG1655 with synonymous UAA codons, which permitted the deletion of release factor 1 and reassignment of UAG translation function. This GRO exhibited improved properties for incorporation of nonstandard amino acids that expand the chemical diversity of proteins in vivo. The GRO also exhibited increased resistance to T7 bacteriophage, demonstrating that new genetic codes could enable increased viral resistance.
Figures
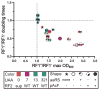
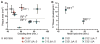
 ) ΔprfA::tolC (ΔA::T); and (×) a clean deletion of prfA (ΔA). (A) RF1 status affects plaque area (Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis of variance, P < 0.001), but strain doubling time does not (Pearson correlation, P = 0.49). Plaque areas (mm2) were calculated with ImageJ, and means ± 95% confidence intervals are reported (n > 12 for each strain). In the absence of RF1, all strains except C0.B*.ΔA::S yielded significantly smaller plaques, indicating that the RF2 variant (16) can terminate UAG adequately to maintain T7 fitness. A statistical summary can be found in table S14. (B) T7 fitness (doublings/hour) (22) is impaired (P = 0.002) and mean lysis time (min) is increased (P < 0.0001) in C321.ΔA compared to C321. Significance was assessed for each metric by using an unpaired t test with Welch’s correction.
) ΔprfA::tolC (ΔA::T); and (×) a clean deletion of prfA (ΔA). (A) RF1 status affects plaque area (Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis of variance, P < 0.001), but strain doubling time does not (Pearson correlation, P = 0.49). Plaque areas (mm2) were calculated with ImageJ, and means ± 95% confidence intervals are reported (n > 12 for each strain). In the absence of RF1, all strains except C0.B*.ΔA::S yielded significantly smaller plaques, indicating that the RF2 variant (16) can terminate UAG adequately to maintain T7 fitness. A statistical summary can be found in table S14. (B) T7 fitness (doublings/hour) (22) is impaired (P = 0.002) and mean lysis time (min) is increased (P < 0.0001) in C321.ΔA compared to C321. Significance was assessed for each metric by using an unpaired t test with Welch’s correction.Similar articles
-
Recoded organisms engineered to depend on synthetic amino acids.Nature. 2015 Feb 5;518(7537):89-93. doi: 10.1038/nature14095. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25607356 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced phosphoserine insertion during Escherichia coli protein synthesis via partial UAG codon reassignment and release factor 1 deletion.FEBS Lett. 2012 Oct 19;586(20):3716-22. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.08.031. Epub 2012 Sep 13. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22982858 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interaction between release factor one and P-site peptidyl-tRNA on the ribosome.J Mol Biol. 1996 Aug 16;261(2):98-107. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0444. J Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8757279
-
Three, four or more: the translational stop signal at length.Mol Microbiol. 1996 Jul;21(2):213-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1996.6391352.x. Mol Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8858577 Review.
-
Termination of protein synthesis.Mol Biol Rep. 1994 May;19(3):171-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00986959. Mol Biol Rep. 1994. PMID: 7969105 Review.
Cited by
-
Directed Evolution of Candidatus Methanomethylophilus alvus Pyrrolysyl-tRNA Synthetase for the Genetic Incorporation of Two Different Noncanonical Amino Acids in One Protein.ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2024 Aug 22;4(5):233-241. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.4c00028. eCollection 2024 Oct 16. ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2024. PMID: 39431264 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning tRNAs for improved translation.Front Genet. 2024 Jun 25;15:1436860. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1436860. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38983271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-specific bioconjugation of an organometallic electron mediator to an enzyme with retained photocatalytic cofactor regenerating capacity and enzymatic activity.Molecules. 2015 Apr 7;20(4):5975-86. doi: 10.3390/molecules20045975. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25853315 Free PMC article.
-
Genomically recoded Escherichia coli with optimized functional phenotypes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 29:2024.08.29.610322. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.29.610322. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39257802 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Recent developments of engineered translational machineries for the incorporation of non-canonical amino acids into polypeptides.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Mar 20;16(3):6513-31. doi: 10.3390/ijms16036513. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25803109 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

