The centrality of RNA for engineering gene expression
- PMID: 24124015
- PMCID: PMC4033574
- DOI: 10.1002/biot.201300018
The centrality of RNA for engineering gene expression
Abstract
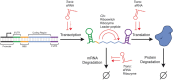
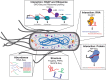
Synthetic biology holds promise as both a framework for rationally engineering biological systems and a way to revolutionize how we fundamentally understand them. Essential to realizing this promise is the development of strategies and tools to reliably and predictably control and characterize sophisticated patterns of gene expression. Here we review the role that RNA can play towards this goal and make a case for why this versatile, designable, and increasingly characterizable molecule is one of the most powerful substrates for engineering gene expression at our disposal. We discuss current natural and synthetic RNA regulators of gene expression acting at key points of control--transcription, mRNA degradation, and translation. We also consider RNA structural probing and computational RNA structure predication tools as a way to study RNA structure and ultimately function. Finally, we discuss how next-generation sequencing methods are being applied to the study of RNA and to the characterization of RNA's many properties throughout the cell.
Keywords: Gene regulation; Next-generation sequencing; Non-coding RNA; RNA structure; Synthetic biology.
© 2013 The Authors. Biotechnology Journal published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Small RNA regulators in bacteria: powerful tools for metabolic engineering and synthetic biology.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Apr;98(8):3413-24. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-5569-y. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24519458 Review.
-
A renaissance in RNA synthetic biology: new mechanisms, applications and tools for the future.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2015 Oct;28:47-56. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2015.05.018. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 26093826 Review.
-
Reprogramming bacteria with RNA regulators.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Oct 31;47(5):1279-1289. doi: 10.1042/BST20190173. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 31642890 Review.
-
Synthetic small RNAs: Current status, challenges, and opportunities.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Dec;119(12):9619-9639. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27252. Epub 2018 Jul 16. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30010218 Review.
-
Design rules of synthetic non-coding RNAs in bacteria.Methods. 2018 Jul 1;143:58-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2018.01.001. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Methods. 2018. PMID: 29309838 Review.
Cited by
-
A universal strategy for regulating mRNA translation in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Apr 30;43(8):4353-62. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv290. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25845589 Free PMC article.
-
Computational design of small transcription activating RNAs for versatile and dynamic gene regulation.Nat Commun. 2017 Oct 19;8(1):1051. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01082-6. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29051490 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA translation and protein synthesis: an analysis of different modelling methodologies and a new PBN based approach.BMC Syst Biol. 2014 Feb 27;8:25. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-8-25. BMC Syst Biol. 2014. PMID: 24576337 Free PMC article.
-
Spatially Restricting Bioorthogonal Nucleoside Biosynthesis Enables Selective Metabolic Labeling of the Mitochondrial Transcriptome.ACS Chem Biol. 2018 Jun 15;13(6):1474-1479. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.8b00262. Epub 2018 May 17. ACS Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29756767 Free PMC article.
-
'Deadman' and 'Passcode' microbial kill switches for bacterial containment.Nat Chem Biol. 2016 Feb;12(2):82-6. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1979. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Nat Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 26641934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Purnick PE, Weiss R. The second wave of synthetic biology: From modules to systems. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009;10:410–422. - PubMed
-
- Cheng AA, Lu TK. Synthetic biology: An emerging engineering discipline. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012;14:155–178. - PubMed
-
- Sharp PA. The centrality of RNA. Cell. 2009;136:577–580. - PubMed
-
- Brantl S. Regulatory mechanisms employed by cis-encoded antisense RNAs. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007;10:102–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

