Metastatic melanoma: lactate dehydrogenase levels and CT imaging findings of tumor devascularization allow accurate prediction of survival in patients treated with bevacizumab
- PMID: 24072776
- PMCID: PMC3985552
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.13130776
Metastatic melanoma: lactate dehydrogenase levels and CT imaging findings of tumor devascularization allow accurate prediction of survival in patients treated with bevacizumab
Abstract
Purpose: To predict survival in patients with metastatic melanoma by evaluating a combination of serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level and initial computed tomographic (CT) findings of tumor devascularization after antiangiogenic therapy.
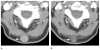
Materials and methods: Consent was waived for this institutional review board-approved, retrospective, secondary analysis. Forty-four patients with metastatic melanoma received bevacizumab therapy in a randomized prospective phase II trial. Target lesions on the initial posttherapy CT images were evaluated by using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors, the Choi criteria, and Morphology, Attenuation, Size, and Structure (MASS) criteria. Cox proportional hazards models were used to assess the association of baseline clinical variables including serum LDH and imaging findings with progression-free and overall survival. The receiver operating characteristic curve with area under the curve (AUC) was used to evaluate accuracy.
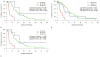
Results: In multivariate analysis, a high baseline serum LDH level was associated with decreased progression-free survival (hazard ratio = 1.29 for each increase of 100 IU/L; P = .002) and overall survival (hazard ratio = 1.44 for each increase of 100 IU/L; P = .001). Evaluation with MASS criteria of the first CT examination after therapy strongly predicted progression-free (P < .001) and overall (P < .001) survival. Baseline serum LDH level was moderately accurate for predicting progression-free survival at 9 months (AUC = 0.793) and overall survival at 18 months (AUC = 0.689). The combination of baseline serum LDH levels and evaluation with MASS criteria at the first CT examination after therapy had significantly higher accuracy for predicting progression-free survival at 9 months (AUC = 0.969) and overall survival at 18 months (AUC = 0.813) than did baseline serum LDH levels alone for prediction of progression-free survival (P = .020).
Conclusion: A combination of baseline serum LDH levels and evaluation with MASS criteria at the first CT examination after bevacizumab therapy had the highest accuracy for predicting survival in patients with metastatic melanoma.
© RSNA, 2013
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Increased visceral to subcutaneous fat ratio is associated with decreased overall survival in patients with metastatic melanoma receiving anti-angiogenic therapy.Surg Oncol. 2015 Dec;24(4):353-8. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26690825 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Predicting Overall Survival in Patients With Metastatic Melanoma on Antiangiogenic Therapy and RECIST Stable Disease on Initial Posttherapy Images Using CT Texture Analysis.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015 Sep;205(3):W283-93. doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.14315. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015. PMID: 26295664 Clinical Trial.
-
Serum lactate dehydrogenase as an early marker for outcome in patients treated with anti-PD-1 therapy in metastatic melanoma.Br J Cancer. 2016 Feb 2;114(3):256-61. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.467. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Br J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26794281 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and outcome of treatment of metastatic melanoma using 3-bromopyruvate: a concise literature review and case study.Chin J Cancer. 2014 Jul;33(7):356-64. doi: 10.5732/cjc.013.10111. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Chin J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24636230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum lactate dehydrogenase is a predictor of poor survival in malignant melanoma.Panminerva Med. 2017 Dec;59(4):332-337. doi: 10.23736/S0031-0808.16.03216-X. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Panminerva Med. 2017. PMID: 27309261 Review.
Cited by
-
The serum LDH level and KELIM scores are potential predictors of a benefit from bevacizumab first-line therapy for patients with advanced ovarian cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2025 Jan;27(1):340-350. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03569-3. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Clin Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 38904923
-
Elevated IgG4 in patient circulation is associated with the risk of disease progression in melanoma.Oncoimmunology. 2015 Jun 3;4(11):e1032492. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1032492. eCollection 2015 Nov. Oncoimmunology. 2015. PMID: 26451312 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound, CT, MRI, or PET-CT for staging and re-staging of adults with cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jul 1;7(7):CD012806. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012806.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31260100 Free PMC article.
-
Increased visceral to subcutaneous fat ratio is associated with decreased overall survival in patients with metastatic melanoma receiving anti-angiogenic therapy.Surg Oncol. 2015 Dec;24(4):353-8. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26690825 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dabrafenib for Treating Unresectable, Advanced or Metastatic BRAF V600 Mutation-Positive Melanoma: An Evidence Review Group Perspective.Pharmacoeconomics. 2015 Sep;33(9):893-904. doi: 10.1007/s40273-015-0276-9. Pharmacoeconomics. 2015. PMID: 25906420 Review.
References
-
- Heakal Y, Kester M, Savage S. Vemurafenib (PLX4032): an orally available inhibitor of mutated BRAF for the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Ann Pharmacother. 2011;45(11):1399–1405. - PubMed
-
- González-Cao M, Viteri S, Díaz-Lagares A, et al. Preliminary results of the combination of bevacizumab and weekly Paclitaxel in advanced melanoma. Oncology. 2008;74(1–2):12–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

