Density dependence in Caenorhabditis larval starvation
- PMID: 24071624
- PMCID: PMC3784960
- DOI: 10.1038/srep02777
Density dependence in Caenorhabditis larval starvation
Abstract
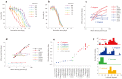
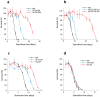
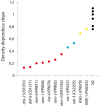
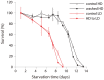
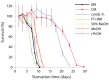
Availability of food is often a limiting factor in nature. Periods of food abundance are followed by times of famine, often in unpredictable patterns. Reliable information about the environment is a critical ingredient of successful survival strategy. One way to improve accuracy is to integrate information communicated by other organisms. To test whether such exchange of information may play a role in determining starvation survival strategies, we studied starvation of L1 larvae in C. elegans and other Caenorhabditis species. We found that some species in genus Caenorhabditis, including C. elegans, survive longer when starved at higher densities, while for others survival is independent of the density. The density effect is mediated by chemical signal(s) that worms release during starvation. This starvation survival signal is independent of ascarosides, a class of small molecules widely used in chemical communication of C. elegans and other nematodes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transgenerational Effects of Early Life Starvation on Growth, Reproduction, and Stress Resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2015 Sep;201(1):201-12. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.178699. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Genetics. 2015. PMID: 26187123 Free PMC article.
-
Starvation-induced collective behavior in C. elegans.Sci Rep. 2015 May 27;5:10647. doi: 10.1038/srep10647. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26013573 Free PMC article.
-
The L-isoaspartyl-O-methyltransferase in Caenorhabditis elegans larval longevity and autophagy.Dev Biol. 2007 Mar 15;303(2):493-500. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.11.023. Epub 2006 Nov 21. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17187774 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical mating cues in C. elegans.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Sep;33:18-24. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24977334 Review.
-
Small molecule signals mediate social behaviors in C. elegans.J Neurogenet. 2020 Sep-Dec;34(3-4):395-403. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2020.1808634. Epub 2020 Sep 29. J Neurogenet. 2020. PMID: 32990104 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transgenerational Effects of Early Life Starvation on Growth, Reproduction, and Stress Resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2015 Sep;201(1):201-12. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.178699. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Genetics. 2015. PMID: 26187123 Free PMC article.
-
The olfactory neuron AWC promotes avoidance of normally palatable food following chronic dietary restriction.J Exp Biol. 2014 May 15;217(Pt 10):1790-8. doi: 10.1242/jeb.099929. Epub 2014 Feb 27. J Exp Biol. 2014. PMID: 24577446 Free PMC article.
-
Small-molecule pheromones and hormones controlling nematode development.Nat Chem Biol. 2017 May 17;13(6):577-586. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2356. Nat Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 28514418 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific developmental gene expression atlas unveils dimorphic gene networks in C. elegans.Nat Commun. 2024 May 20;15(1):4273. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48369-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38769103 Free PMC article.
-
Experience Modulates the Reproductive Response to Heat Stress in C. elegans via Multiple Physiological Processes.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 29;10(12):e0145925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145925. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26713620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eijkelenboom A. & Burgering B. M. FOXOs: signalling integrators for homeostasis maintenance. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 14, 83–97 (2013). - PubMed
-
- van der Horst A. & Burgering B. M. Stressing the role of FoxO proteins in lifespan and disease. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 440–450 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Avogaro A., de Kreutzenberg S. V. & Fadini G. P. Insulin signaling and life span. Pflugers Ar. Eur J. Physiol. 459, 301–314 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Taguchi A. & White M. F. Insulin-like signaling, nutrient homeostasis, and life span. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 70, 191–212 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

