Plakophilin-1 protects keratinocytes from pemphigus vulgaris IgG by forming calcium-independent desmosomes
- PMID: 24056861
- PMCID: PMC3961504
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2013.401
Plakophilin-1 protects keratinocytes from pemphigus vulgaris IgG by forming calcium-independent desmosomes
Abstract
Plakophilin-1 (PKP-1) is an armadillo family protein critical for desmosomal adhesion and epidermal integrity. In the autoimmune skin-blistering disease pemphigus vulgaris (PV), autoantibodies (IgG) target the desmosomal cadherin desmoglein 3 (Dsg3) and compromise keratinocyte cell-cell adhesion. Here, we report that enhanced expression of PKP-1 protects keratinocytes from PV IgG-induced loss of cell-cell adhesion. PKP-1 prevents loss of Dsg3 and other desmosomal proteins from cell-cell borders and prevents alterations in desmosome ultrastructure in keratinocytes treated with PV IgG. Using a series of Dsg3 chimeras and deletion constructs, we find that PKP-1 clusters Dsg3 with the desmosomal plaque protein desmoplakin in a manner dependent on the plakoglobin-binding domain of the Dsg3 tail. Furthermore, PKP-1 expression transforms desmosome adhesion from a calcium-dependent to a calcium-independent and hyperadhesive state. These results demonstrate that manipulating the expression of a single desmosomal plaque protein can block the pathogenic effects of PV IgG on keratinocyte adhesion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
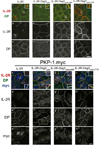
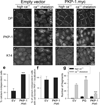
Comment in
-
Plakophilins, desmogleins, and pemphigus: the tail wagging the dog.J Invest Dermatol. 2014 Apr;134(4):874-876. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.491. J Invest Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24646797 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Plakophilins, desmogleins, and pemphigus: the tail wagging the dog.J Invest Dermatol. 2014 Apr;134(4):874-876. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.491. J Invest Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24646797 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into desmosome regulation and pemphigus blistering as a desmosome-remodeling disease.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2013 Jan;29(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2012.08.001. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23257250 Review.
-
Desmoglein endocytosis and desmosome disassembly are coordinated responses to pemphigus autoantibodies.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 17;281(11):7623-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512447200. Epub 2005 Dec 23. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16377623
-
Pemphigus vulgaris IgG-induced desmoglein-3 endocytosis and desmosomal disassembly are mediated by a clathrin- and dynamin-independent mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 27;283(26):18303-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M710046200. Epub 2008 Apr 23. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18434319 Free PMC article.
-
Pemphigus: a Comprehensive Review on Pathogenesis, Clinical Presentation and Novel Therapeutic Approaches.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018 Feb;54(1):1-25. doi: 10.1007/s12016-017-8662-z. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29313220 Review.
Cited by
-
Desmosome regulation and signaling in disease.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Jun;360(3):501-12. doi: 10.1007/s00441-015-2136-5. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 25693896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular organization of the desmosome as revealed by direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy.J Cell Sci. 2016 Aug 1;129(15):2897-904. doi: 10.1242/jcs.185785. Epub 2016 Jun 17. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 27505428 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular architecture of the desmosomal outer dense plaque by integrative structural modeling.Protein Sci. 2024 Dec;33(12):e5217. doi: 10.1002/pro.5217. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 39548826 Free PMC article.
-
Super-Resolution Microscopy Reveals Altered Desmosomal Protein Organization in Tissue from Patients with Pemphigus Vulgaris.J Invest Dermatol. 2016 Jan;136(1):59-66. doi: 10.1038/JID.2015.353. J Invest Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 26763424 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Disease: Pemphigus and Bullous Pemphigoid.Annu Rev Pathol. 2016 May 23;11:175-97. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-012615-044313. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Annu Rev Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26907530 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Amoudi A, Diez DC, Betts MJ, Frangakis AS. The molecular architecture of cadherins in native epidermal desmosomes. Nature. 2007;450:832–837. - PubMed
-
- Amagai M, Klaus-Kovtun V, Stanley JR. Autoantibodies against a novel epithelial cadherin in pemphigus vulgaris, a disease of cell adhesion. Cell. 1991;67:869–877. - PubMed
-
- Bornslaeger EA, Godsel LM, Corcoran CM, Park JK, Hatzfeld M, Kowalczyk AP, et al. Plakophilin 1 interferes with plakoglobin binding to desmoplakin, yet together with plakoglobin promotes clustering of desmosomal plaque complexes at cell-cell borders. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:727–738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

