Serum biomarkers of immune activation and subsequent risk of non-hodgkin B-cell lymphoma among HIV-infected women
- PMID: 24045923
- PMCID: PMC3833437
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-13-0614
Serum biomarkers of immune activation and subsequent risk of non-hodgkin B-cell lymphoma among HIV-infected women
Abstract
Background: There is increasing evidence that chronic immune activation predisposes to non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Whether this association exists among women representative of the current HIV epidemic in the United States who are at high risk of HIV-associated NHL (AIDS-NHL), remains to be determined.
Methods: We conducted a nested case-control study within the Women's Interagency HIV Study with longitudinally collected risk factor data and sera. Cases were HIV-infected women with stored sera collected at three time-windows 3 to 5 years, 1 to 3 years, and 0 to 1 year before AIDS-NHL diagnosis (n = 22). Three to six HIV-infected controls, without AIDS-NHL, were matched to each case on age, race, CD4(+) T-cell count, and study follow-up time (n = 78). ORs and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for the association between one unit increase in log-transformed biomarker levels and AIDS-NHL were computed using random effect multivariate logistic regression models.
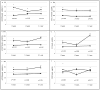
Results: Elevated levels of sCD27 (OR = 7.21; 95% CI, 2.62-19.88), sCD30 (OR = 2.64; 95% CI, 1.24-5.64), and CXCL13 (OR = 2.56; 95% CI, 1.32-4.96) were associated with subsequent diagnosis of AIDS-NHL overall. Elevated sCD23 was associated with a two to three-fold increased risk of AIDS-NHL in certain subgroups, whereas elevated interleukin 6 was associated with a two-fold increased risk in the 0 to 1 year time-window, only.
Conclusions: These findings support the hypothesis that chronic B-cell activation contributes to the development of AIDS-NHL in women.
Impact: Soluble CD23 (sCD23), sCD27, sCD30, and CXCL13 may serve as biomarkers for AIDS-NHL.
©2013 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Markers of Immune Activation and Inflammation, and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies.JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2018 Dec;2(4):pky082. doi: 10.1093/jncics/pky082. Epub 2019 Mar 5. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2018. PMID: 30873511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum levels of cytokines and biomarkers for inflammation and immune activation, and HIV-associated non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma risk.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014 Feb;23(2):343-9. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-13-0714. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014. PMID: 24220912 Free PMC article.
-
B-cell stimulatory cytokines and markers of immune activation are elevated several years prior to the diagnosis of systemic AIDS-associated non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011 Jul;20(7):1303-14. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-11-0037. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011. PMID: 21527584 Free PMC article.
-
Serum levels of the chemokine CXCL13, genetic variation in CXCL13 and its receptor CXCR5, and HIV-associated non-hodgkin B-cell lymphoma risk.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2013 Feb;22(2):295-307. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-12-1122. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2013. PMID: 23250934 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Microbial Translocation and Immune Activation in AIDS-Associated Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Pathogenesis: What Have We Learned?Crit Rev Immunol. 2020;40(1):41-51. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2020033319. Crit Rev Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32421978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dysregulated B-cell TLR2 expression and elevated regulatory B-cell frequency precede the diagnosis of AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma.AIDS. 2015 Aug 24;29(13):1659-64. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000687. AIDS. 2015. PMID: 26372276 Free PMC article.
-
B-cell and T-cell activation in South African HIV-1-positive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma patients.South Afr J HIV Med. 2018 Nov 7;19(1):809. doi: 10.4102/sajhivmed.v19i1.809. eCollection 2018. South Afr J HIV Med. 2018. PMID: 30473875 Free PMC article.
-
Follicular CD8+ T Cells Are Elevated in HIV Infection and Induce PD-L1 on B Cells.J Immunol. 2023 Jan 1;210(1):33-39. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200194. J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36445393 Free PMC article.
-
Markers of Immune Activation and Inflammation, and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies.JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2018 Dec;2(4):pky082. doi: 10.1093/jncics/pky082. Epub 2019 Mar 5. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2018. PMID: 30873511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum levels of cytokines and biomarkers for inflammation and immune activation, and HIV-associated non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma risk.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014 Feb;23(2):343-9. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-13-0714. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014. PMID: 24220912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grulich AE, Li YM, McDonald AM, Correll PK, Law MG, Kaldor JM. Decreasing rates of Kaposi’s sarcoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in the era of potent combination antiretroviral therapy. AIDS. 2001;15:629–33. - PubMed
-
- Epeldegui M, Widney DP, Martinez-Maza O. Pathogenesis of AIDS lymphoma: role of oncogenic viruses and B cell activation-associated molecular lesions. Curr Opin Oncol. 2006;18:444–8. - PubMed
-
- Marks MA, Rabkin CS, Engels EA, Busch E, Kopp W, Rager H, et al. Markers of microbial translocation and risk of AIDS-related lymphoma. AIDS. 2013;27(3):469–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K07 CA140360/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA168482/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI028697/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD032632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

