Effects of sulfonylureas on tumor growth: a review of the literature
- PMID: 24043597
- PMCID: PMC3805154
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2013-0177
Effects of sulfonylureas on tumor growth: a review of the literature
Abstract
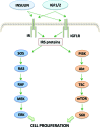
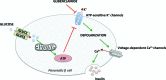
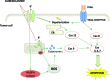
Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients are at higher cancer risk, probably because of hyperinsulinemia and insulin growth factor 1 pathway activation. The effects of antidiabetic drugs on cancer risk have been described and discussed in several studies suggesting opposite effects of the biguanide metformin and sulfonylureas on cancer incidence and mortality. The anticancer mechanisms of metformin have been clarified, and some clinical studies, particularly in breast cancer patients, have been published or are currently ongoing; however, data about the effects of sulfonylureas on cancer growth are less consistent. The aims of this work are to review preclinical evidence of second-generation sulfonylureas effects on tumor growth, to clarify the potential mechanisms of action, and to identify possible metabolic targets for patient selection. Most evidence is on the adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels inhibitor glibenclamide, which interacts with reactive oxygen species production thus inducing cancer cell death. Among diarylsulfonylureas, next-generation DW2282 derivatives are particularly promising because of the proapoptotic activity in multidrug-resistant cells.
Keywords: Anticancer agents; Apoptosis; Glibenclamide; Sulfonylurea compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of potential conflicts of interest may be found at the end of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New insights into antidiabetic drugs: Possible applications in cancer treatment.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2017 Dec;90(6):1056-1066. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13013. Epub 2017 Jul 23. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2017. PMID: 28456998 Review.
-
[Diabetes and cancer risk: oncologic considerations].Orv Hetil. 2011 Jul 17;152(29):1144-55. doi: 10.1556/OH.2011.29158. Orv Hetil. 2011. PMID: 21712179 Review. Hungarian.
-
Metformin and sulfonylureas in relation to cancer risk in type II diabetes patients: a meta-analysis using primary data of published studies.Metabolism. 2013 Jul;62(7):922-34. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.01.014. Epub 2013 Feb 16. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 23419783 Review.
-
Race, ethnicity, and use of thiazolidinediones among US adults with diabetes.Curr Med Res Opin. 2007 Mar;23(3):489-94. doi: 10.1185/030079906X167354. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007. PMID: 17355730
-
Enemies or weapons in hands: investigational anti-diabetic drug glibenclamide and cancer risk.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017 Jul;26(7):853-864. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2017.1333104. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28541801 Review.
Cited by
-
Associations between Diabetes Mellitus and Selected Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 8;25(13):7476. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137476. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin, Diabetes, and Survival among U.S. Veterans with Colorectal Cancer.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2016 Oct;25(10):1418-1425. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-16-0312. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2016. PMID: 27496094 Free PMC article.
-
Towards an Integral Therapeutic Protocol for Breast Cancer Based upon the New H+-Centered Anticancer Paradigm of the Late Post-Warburg Era.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 10;21(20):7475. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207475. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33050492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A New and Integral Approach to the Etiopathogenesis and Treatment of Breast Cancer Based upon Its Hydrogen Ion Dynamics.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 7;21(3):1110. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031110. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32046158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic Review with Network Meta-Analysis: Antidiabetic Medication and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 19;6:33743. doi: 10.1038/srep33743. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27642100 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Noto H, Tsujimoto T, Sasazuki T, et al. Significantly increased risk of cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocr Pract. 2011;17:616–628. - PubMed
-
- Vigneri P, Frasca F, Sciacca L, et al. Diabetes and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2009;16:1103–1123. - PubMed
-
- Gandini S, Guerrieri-Gonzaga A, Puntoni M, et al. Metformin and breast cancer risk. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:973–974. - PubMed
-
- Pollak M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:915–928. - PubMed
-
- Monami M, Lamanna C, Balzi D, et al. Sulphonylureas and cancer: A case-control study. Acta Diabetol. 2009;46:279–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

