A novel multilayered multidisk oral tablet for chronotherapeutic drug delivery
- PMID: 24024200
- PMCID: PMC3762207
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/569470
A novel multilayered multidisk oral tablet for chronotherapeutic drug delivery
Abstract
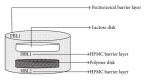
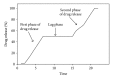
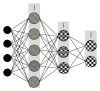
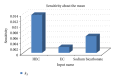
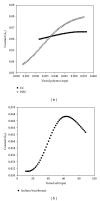
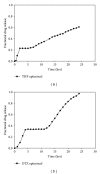
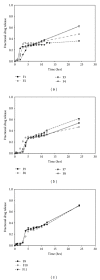
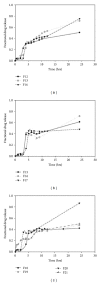
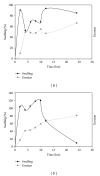
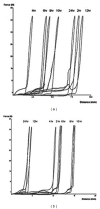
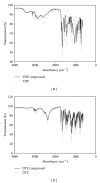
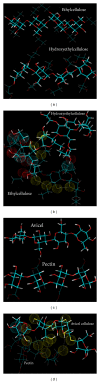
A Multilayered Multidisk Tablet (MLMDT) comprising two drug-loaded disks enveloped by three drug-free barrier layers was developed for use in chronotherapeutic disorders, employing two model drugs, theophylline and diltiazem HCl. The MLMDT was designed to achieve two pulses of drug release separated by a lag phase. The polymer disk comprised hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) and ethylcellulose (EC) granulated using an aqueous dispersion of EC. The polymeric barrier layers constituted a combination of pectin/Avicel (PBL) (1st barrier layer) and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) (HBL1 and HBL2) as the 2nd and 3rd barrier layers, respectively. Sodium bicarbonate was incorporated into the diltiazem-containing formulation for delayed drug release. Erosion and swelling studies confirmed the manner in which the drug was released with theophylline formulations exhibiting a maximum swelling of 97% and diltiazem containing formulations with a maximum swelling of 119%. FTIR spectra displayed no interactions between drugs and polymers. Molecular mechanics simulations were undertaken to predict the possible orientation of the polymer morphologies most likely affecting the MLMDT performance. The MLMDT provided two pulses of drug release, separated by a lag phase, and additionally it displayed desirable friability, hardness, and uniformity of mass indicating a stable formulation that may be a desirable candidate for chronotherapeutic drug delivery.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A new ternary polymeric matrix system for controlled drug delivery of highly soluble drugs: I. Diltiazem hydrochloride.Pharm Res. 1997 Oct;14(10):1415-21. doi: 10.1023/a:1012124806316. Pharm Res. 1997. PMID: 9358555
-
Development and release mechanism of diltiazem HCl prolonged release matrix tablets.Drug Deliv. 2009 Feb;16(2):67-74. doi: 10.1080/10717540802586220. Drug Deliv. 2009. PMID: 19267297
-
In vitro release of ketoprofen from hydrophilic matrix tablets containing cellulose polymer mixtures.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2013 Nov;39(11):1651-62. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2012.729146. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23094867
-
Role of cellulose ether polymers on ibuprofen release from matrix tablets.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2005 Aug;31(7):653-65. doi: 10.1080/03639040500216360. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2005. PMID: 16207613
-
[Preparation of diltiazem hydrochloride delayed-onset, sustained release tablet].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2002 Sep;37(9):724-7. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2002. PMID: 12567900 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Compression-coated pulsatile chronomodulated therapeutic system: QbD assisted optimization.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):2258-2268. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2094500. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35838522 Free PMC article.
-
In silico analytico-mathematical interpretation of biopolymeric assemblies: Quantification of energy surfaces and molecular attributes via atomistic simulations.Bioeng Transl Med. 2018 Sep 26;3(3):222-231. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10105. eCollection 2018 Sep. Bioeng Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30377662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systems Chronotherapeutics.Pharmacol Rev. 2017 Apr;69(2):161-199. doi: 10.1124/pr.116.013441. Pharmacol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28351863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrical Field-Assisted Gene Delivery from Polyelectrolyte Multilayers.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Jan 6;12(1):133. doi: 10.3390/polym12010133. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31935814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bahammam A, Alrajeh M, Albabtain M, Bahammam S, Sharif M. Circadian pattern of sleep, energy expenditure, and body temperature of young healthy men during the intermittent fasting of Ramadan. Appetite. 2010;54(2):426–429. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh C-H, Ohman MD. Biological responses to environmental forcing: the linear tracking window hypothesis. Ecology. 2006;87(8):1932–1938. - PubMed
-
- Rosenwasser AM. Circadian clock genes: non-circadian roles in sleep, addiction, and psychiatric disorders? Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 2010;34(8):1249–1255. - PubMed
-
- Sewlall S, Pillay V, Danckwerts MP, Choonara YE, Ndesendo VMK, du Toit LC. A timely review of state-of-the-art chronopharmaceuticals synchronized with biological rhythms. Current Drug Delivery. 2010;7(5):370–388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

