TLR2 regulates neutrophil recruitment and cytokine production with minor contributions from TLR9 during hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- PMID: 24023674
- PMCID: PMC3758260
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073143
TLR2 regulates neutrophil recruitment and cytokine production with minor contributions from TLR9 during hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Abstract
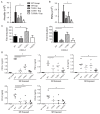
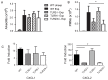
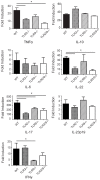
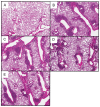
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is an interstitial lung disease that develops following repeated exposure to environmental antigens. The disease results in alveolitis, granuloma formation and may progress to a fibrotic chronic form, which is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. The severity of the disease correlates with a neutrophil rich influx and an IL-17 response. We used the Saccharopolysporarectivirgula (SR) model of HP to determine whether Toll-like receptors (TLR) 2 and 9 cooperate in neutrophil recruitment and IL-17-associated cytokine production during the development of HP. Stimulation of bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs) from C57BL/6, MyD88(-/-) and TLR2/9(-/-) mice with SR demonstrate that SR is a strong inducer of neutrophil chemokines and growth factors. The cytokines induced by SR were MyD88-dependent and, of those, most were partially or completely dependent on TLRs 2 and 9. Following in vivo exposure to SR, CXCL2 production and neutrophil recruitment were reduced in TLR2(-/-) and TLR2/9(-/-) mice suggesting that the response was largely dependent on TLR2; however the reduction was greatest in the TLR2/9(-/-) double knockout mice indicating TLR9 may also contribute to the response. There was a reduction in the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNFα and IL-6 as well as CCL3 and CCL4 in the BALF from TLR2/9(-/-) mice compared to WT and single knockout (SKO) mice exposed one time to SR. The decrease in neutrophil recruitment and TNFα production in the TLR2/9(-/-) mice was maintained throughout 3 weeks of SR exposures in comparison to WT and SKO mice. Both TLRs 2 and 9 contributed to the Th17 response; there was a decrease in Th17 cells and IL-17 mRNA in the TLR2/9(-/-) mice in comparison to the WT and SKO mice. Despite the effects on neutrophil recruitment and the IL-17 response, TLR2/9(-/-) mice developed granuloma formation similarly to WT and SKO mice suggesting that there are additional mediators and pattern recognition receptors involved in the disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protein kinase D1 in myeloid lineage cells contributes to the accumulation of CXCR3+CCR6+ nonconventional Th1 cells in the lungs and potentiates hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by S. rectivirgula.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 11;15:1403155. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1403155. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39464896 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by Saccharopolyspora rectivirgula is not associated with a switch to a Th2 response.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Mar 1;310(5):L393-402. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00305.2015. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26719148 Free PMC article.
-
MyD88 is necessary for neutrophil recruitment in hypersensitivity pneumonitis.J Leukoc Biol. 2008 May;83(5):1207-17. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0607391. Epub 2008 Feb 19. J Leukoc Biol. 2008. PMID: 18285403 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine production during hypersensitivity pneumonitis.Eur J Immunol. 2004 Mar;34(3):677-685. doi: 10.1002/eji.200324634. Eur J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14991597
-
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis and alpha-chemokines.Clin Ter. 2017 Mar-Apr;168(2):e140-e145. doi: 10.7417/CT.2017.1996. Clin Ter. 2017. PMID: 28383627 Review.
Cited by
-
Intrarenal Toll-like receptor 4 and Toll-like receptor 2 expression correlates with injury in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):F1283-F1294. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00040.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29923769 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in Porphyromonas gingivalis LPS-treated mouse macrophage cell line (RAW264.7) requires Toll-like receptor 9.Inflamm Res. 2018 Sep;67(9):723-726. doi: 10.1007/s00011-018-1168-1. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 29980803
-
Protein kinase D1 in myeloid lineage cells contributes to the accumulation of CXCR3+CCR6+ nonconventional Th1 cells in the lungs and potentiates hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by S. rectivirgula.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 11;15:1403155. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1403155. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39464896 Free PMC article.
-
Longstanding hypersensitivity pneumonitis and its response to roflumilast: A review of its likely immunological effects.Respir Med Case Rep. 2022 Jul 20;39:101701. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2022.101701. eCollection 2022. Respir Med Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35942000 Free PMC article.
-
A critical role of Dectin-1 in hypersensitivity pneumonitis.Inflamm Res. 2016 Mar;65(3):235-44. doi: 10.1007/s00011-015-0910-1. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Inflamm Res. 2016. PMID: 26644324
References
-
- Salvaggio JE, deShazo RD (1986) Pathogenesis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest 89: 190S-193S. doi:10.1378/chest.89.3_Supplement.190S. PubMed: 3948579. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ando M, Suga M (1997) Hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Curr Opin Pulm Med 3: 391-395. doi:10.1097/00063198-199709000-00013. PubMed: 9331543. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

