Evaluation of extended interval dosing aminoglycosides in the morbidly obese population
- PMID: 24023540
- PMCID: PMC3760189
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/194389
Evaluation of extended interval dosing aminoglycosides in the morbidly obese population
Abstract
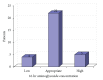
Aminoglycoside dosing has been studied in the obese population, typically recommending an adjusted weight utilizing a 40% dosing weight correction factor (IBW + 0.4 × (TBW-IBW)). These studies included limited numbers of morbidly obese patients and were not done in the era of extended interval aminoglycoside dosing. Here, we report a retrospective evaluation of morbidly obese patients receiving gentamicin or tobramycin at our hospital. The objective of this study was to evaluate the accuracy of the commonly recommended adjusted weight for weight-based dosing. There were 31 morbidly obese patients who received gentamicin or tobramycin 5-7 mg/kg every 24 hours using a 40% dosing weight correction factor. Our institution utilizes 16-hour postdose concentrations to monitor extended interval aminoglycosides. Twenty-two of the 31 patients (71%) achieved an appropriate serum drug concentration. Four patients (13%) were found to be supratherapeutic and 5 patients (16%) subtherapeutic. The only variable that correlated with supratherapeutic levels was older age (P = 0.0378). Our study helps to validate the current dosing weight correction factor (40%) in the morbidly obese population. We recommend caution when dosing aminoglycosides in morbidly obese patients who are of older age.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aminoglycoside dosing weight correction factors for patients of various body sizes.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995 Feb;39(2):545-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.39.2.545. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995. PMID: 7726530 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of weight on aminoglycoside pharmacokinetics in normal weight and morbidly obese patients.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;24(5):643-7. doi: 10.1007/BF00542215. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1983. PMID: 6873144
-
Vancomycin dosing in morbidly obese patients.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1998 Oct;54(8):621-5. doi: 10.1007/s002280050524. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9860149
-
Unfractionated heparin dosing for venous thromboembolism in morbidly obese patients: case report and review of the literature.Pharmacotherapy. 2010 Mar;30(3):324. doi: 10.1592/phco.30.3.324. Pharmacotherapy. 2010. PMID: 20180615 Review.
-
Impact of hospital guideline for weight-based antimicrobial dosing in morbidly obese adults and comprehensive literature review.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2014 Dec;39(6):584-608. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12200. Epub 2014 Sep 9. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2014. PMID: 25203631 Review.
Cited by
-
Aminoglycoside-Related Nephrotoxicity and Ototoxicity in Clinical Practice: A Review of Pathophysiological Mechanism and Treatment Options.Adv Ther. 2023 Apr;40(4):1357-1365. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02436-x. Epub 2023 Feb 4. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 36738370 Review.
-
Pharmacokinetic changes and dosing modification of aminoglycosides in critically ill obese patients: a literature review.J Clin Med Res. 2014 Aug;6(4):227-33. doi: 10.14740/jocmr1858w. Epub 2014 May 22. J Clin Med Res. 2014. PMID: 24883145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic management of peritonitis: a comprehensive guide for intensivists.Intensive Care Med. 2016 Aug;42(8):1234-47. doi: 10.1007/s00134-016-4307-6. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Intensive Care Med. 2016. PMID: 26984317
-
Antibiotic therapy of pneumonia in the obese patient: dosing and delivery.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2014 Apr;27(2):165-73. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000045. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24504134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Gentamicin in Various Patient Populations and Consequences for Optimal Dosing for Gram-Negative Infections: An Updated Review.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022 Aug;61(8):1075-1094. doi: 10.1007/s40262-022-01143-0. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022. PMID: 35754071 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The World Health Organization. Obesity Fact Sheet. March 2013, http://www.who.int/topics/obesity/en/
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Adult Obesity Facts. March 2013, http://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/adult.html.
-
- Pai MP, Bearden DT. Antimicrobial dosing considerations in obese adult patients: insights from the society of infectious diseases pharmacists. Pharmacotherapy. 2007;27(8):1081–1091. - PubMed
-
- Newman D, Scheetz MH, Adeyemi OA, et al. Serum piperacillin/tazobactam pharmacokinetics in a morbidly obese individual. Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 2007;41(10):1734–1739. - PubMed
-
- Lee JB, Winstead S, Cook AM. Pharmacokinetic alterations in obesity. Orthopedics. 2006;29(11):984–988. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources