Stress-induced recruitment of bone marrow-derived monocytes to the brain promotes anxiety-like behavior
- PMID: 23966702
- PMCID: PMC3755721
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1671-13.2013
Stress-induced recruitment of bone marrow-derived monocytes to the brain promotes anxiety-like behavior
Abstract
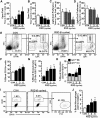
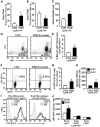
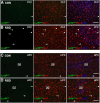
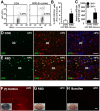
Social stress is associated with altered immunity and higher incidence of anxiety-related disorders. Repeated social defeat (RSD) is a murine stressor that primes peripheral myeloid cells, activates microglia, and induces anxiety-like behavior. Here we show that RSD-induced anxiety-like behavior corresponded with an exposure-dependent increase in circulating monocytes (CD11b(+)/SSC(lo)/Ly6C(hi)) and brain macrophages (CD11b(+)/SSC(lo)/CD45(hi)). Moreover, RSD-induced anxiety-like behavior corresponded with brain region-dependent cytokine and chemokine responses involved with myeloid cell recruitment. Next, LysM-GFP(+) and GFP(+) bone marrow (BM)-chimeric mice were used to determine the neuroanatomical distribution of peripheral myeloid cells recruited to the brain during RSD. LysM-GFP(+) mice showed that RSD increased recruitment of GFP(+) macrophages to the brain and increased their presence within the perivascular space (PVS). In addition, RSD promoted recruitment of GFP(+) macrophages into the PVS and parenchyma of the prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus of GFP(+) BM-chimeric mice. Furthermore, mice deficient in chemokine receptors associated with monocyte trafficking [chemokine receptor-2 knockout (CCR2(KO)) or fractalkine receptor knockout (CX3CR1(KO))] failed to recruit macrophages to the brain and did not develop anxiety-like behavior following RSD. Last, RSD-induced macrophage trafficking was prevented in BM-chimeric mice generated with CCR2(KO) or CX3CR1(KO) donor cells. These findings indicate that monocyte recruitment to the brain in response to social stress represents a novel cellular mechanism that contributes to the development of anxiety.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spatio-temporal profile, phenotypic diversity, and fate of recruited monocytes into the post-ischemic brain.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Nov 4;13(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0750-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27814740 Free PMC article.
-
β-Adrenergic receptor antagonism prevents anxiety-like behavior and microglial reactivity induced by repeated social defeat.J Neurosci. 2011 Apr 27;31(17):6277-88. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0450-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21525267 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of interleukin-1 receptor type-1 on endothelial cells attenuated stress-induced neuroinflammation and prevented anxiety-like behavior.J Neurosci. 2014 Feb 12;34(7):2583-91. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3723-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24523548 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral and central effects of repeated social defeat stress: monocyte trafficking, microglial activation, and anxiety.Neuroscience. 2015 Mar 19;289:429-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.01.001. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25596319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular players that shape evolving pathology and neurodegeneration following traumatic brain injury.Brain Behav Immun. 2018 Jul;71:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.03.033. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Brain Behav Immun. 2018. PMID: 29601944 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-1 Receptor-1 on Vglut2 + neurons in the hippocampus is critical for neuronal and behavioral sensitization after repeated social stress.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022 Oct 29;26:100547. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2022.100547. eCollection 2022 Dec. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022. PMID: 36388133 Free PMC article.
-
Stress induces the danger-associated molecular pattern HMGB-1 in the hippocampus of male Sprague Dawley rats: a priming stimulus of microglia and the NLRP3 inflammasome.J Neurosci. 2015 Jan 7;35(1):316-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3561-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25568124 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling integrated stress, sleep, fear and neuroimmune responses: Relevance for understanding trauma and stress-related disorders.Neurobiol Stress. 2023 Jan 23;23:100517. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2023.100517. eCollection 2023 Mar. Neurobiol Stress. 2023. PMID: 36793998 Free PMC article.
-
Dcf1 Deficiency Attenuates the Role of Activated Microglia During Neuroinflammation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Jul 30;11:256. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00256. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30104955 Free PMC article.
-
Stressor-Induced Reduction in Cognitive Behavior is Associated with Impaired Colonic Mucus Layer Integrity and is Dependent Upon the LPS-Binding Protein Receptor CD14.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Mar 3;15:1617-1635. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S332793. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35264870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beumer W, Gibney SM, Drexhage RC, Pont-Lezica L, Doorduin J, Klein HC, Steiner J, Connor TJ, Harkin A, Versnel MA, Drexhage HA. The immune theory of psychiatric diseases: a key role for activated microglia and circulating monocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 2012;92:959–975. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0212100. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
