The human adenovirus 5 L4 promoter is activated by cellular stress response protein p53
- PMID: 23966406
- PMCID: PMC3807333
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01924-13
The human adenovirus 5 L4 promoter is activated by cellular stress response protein p53
Abstract
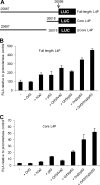
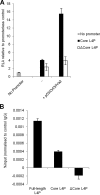
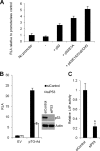
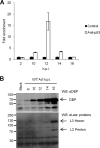
During adenovirus infection, the emphasis of gene expression switches from early genes to late genes in a highly regulated manner. Two gene products, L4-22K and L4-33K, contribute to this switch by activating the major late transcription unit (MLTU) and regulating the splicing of its transcript. L4-22K and L4-33K expression is driven initially by a recently described L4 promoter (L4P) embedded within the MLTU that is activated by early and intermediate viral factors: E1A, E4 Orf3, and IVa2. Here we show that this promoter is also significantly activated by the cellular stress response regulator, p53. Exogenous expression of p53 activated L4P in reporter assays, while depletion of endogenous p53 inhibited the induction of L4P by viral activators. Chromatin immunoprecipitation studies showed that p53 associates with L4P and that during adenovirus type 5 (Ad5) infection, this association peaks at 12 h postinfection, coinciding with the phase of the infectious cycle when L4P is active, and is then lost as MLP activation commences. p53 activation of L4P is significant during Ad5 infection, since depletion of p53 prior to infection of either immortalized or normal cells led to severely reduced late gene expression. The association of p53 with L4P is transient due to the action of products of L4P activity (L4-22K/33K), which establish a negative feedback loop that ensures the transient activity of L4P at the start of the late phase and contributes to an efficient switch from early- to late-phase virus gene expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Human Adenovirus Type 5 L4 Promoter Is Negatively Regulated by TFII-I and L4-33K.J Virol. 2015 Jul;89(14):7053-63. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00683-15. Epub 2015 Apr 29. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25926634 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus serotype 5 L4-22K and L4-33K proteins have distinct functions in regulating late gene expression.J Virol. 2009 Apr;83(7):3049-58. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02455-08. Epub 2009 Jan 28. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19176628 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus late-phase infection is controlled by a novel L4 promoter.J Virol. 2010 Jul;84(14):7096-104. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00107-10. Epub 2010 May 5. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20444889 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of human adenovirus alternative RNA splicing by the adenoviral L4-33K and L4-22K proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jan 28;16(2):2893-912. doi: 10.3390/ijms16022893. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25636034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetically modified adenoviruses against gliomas: from bench to bedside.Neurology. 2004 Aug 10;63(3):418-26. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000133302.15022.7f. Neurology. 2004. PMID: 15304571 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation of Viral Replication Compartment-enriched Sub-nuclear Fractions from Adenovirus-infected Normal Human Cells.J Vis Exp. 2015 Nov 12;(105):53296. doi: 10.3791/53296. J Vis Exp. 2015. PMID: 26649626 Free PMC article.
-
The Human Adenovirus Type 5 L4 Promoter Is Negatively Regulated by TFII-I and L4-33K.J Virol. 2015 Jul;89(14):7053-63. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00683-15. Epub 2015 Apr 29. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25926634 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Control by DNA Tumor Virus-Encoded Proteins.Pathogens. 2021 May 6;10(5):560. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10050560. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34066504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E1B-55K Is a Phosphorylation-Dependent Transcriptional and Posttranscriptional Regulator of Viral Gene Expression in Human Adenovirus C5 Infection.J Virol. 2022 Mar 9;96(5):e0206221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02062-21. Epub 2022 Jan 12. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35019711 Free PMC article.
-
The Adenovirus E4-ORF3 Protein Stimulates SUMOylation of General Transcription Factor TFII-I to Direct Proteasomal Degradation.mBio. 2016 Jan 26;7(1):e02184-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02184-15. mBio. 2016. PMID: 26814176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Russell WC. 2000. Update on adenovirus and its vectors. J. Gen. Virol. 81:2573–2604 - PubMed
-
- Huang W, Kiefer J, Whalen D, Flint SJ. 2003. DNA synthesis-dependent relief of repression of transcription from the adenovirus type 2 IVa2 promoter by a cellular protein. Virology 314:394–402 - PubMed
-
- Binger MH, Flint SJ. 1984. Accumulation of early and intermediate mRNA species during subgroup C adenovirus productive infections. Virology 136:387–403 - PubMed
-
- Nevins JR, Wilson MC. 1981. Regulation of adenovirus-2 gene expression at the level of transcriptional termination and RNA processing. Nature 290:113–118 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

