Genetic variation near IRF8 is associated with serologic and cytokine profiles in systemic lupus erythematosus and multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 23965942
- PMCID: PMC3856198
- DOI: 10.1038/gene.2013.42
Genetic variation near IRF8 is associated with serologic and cytokine profiles in systemic lupus erythematosus and multiple sclerosis
Abstract
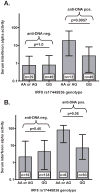
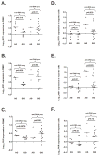
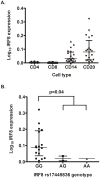
Alleles of interferon (IFN) regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) are associated with susceptibility to both systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and multiple sclerosis (MS). Although high-type I IFN is thought to be causal in SLE, type I IFN is used as a therapy in MS. We investigated whether IRF8 alleles were associated with type I IFN levels or serologic profiles in SLE and MS. Alleles that have been previously associated with SLE or MS were genotyped in SLE and MS patients. The MS-associated rs17445836G allele was associated with anti-double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) autoantibodies in SLE patients (meta-analysis odds ratio=1.92). The same allele was associated with decreased serum IFN activity in SLE patients with anti-dsDNA antibodies, and with decreased type I IFN-induced gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cell from anti-dsDNA-negative SLE patients. In secondary progressive MS patients, rs17445836G was associated with decreased serum type I IFN. Rs17445836G was associated with increased IRF8 expression in SLE patient B cells. In summary, IRF8 rs17445836G is associated with human autoimmune disease characterized by low-type I IFN levels, and this may have pharmacogenetic relevance as type I IFN is modulated in SLE and MS. The association with autoantibodies and increased IRF8 expression in B cells supports a role for rs17445836G in humoral tolerance.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Interferon regulatory factors in human lupus pathogenesis.Transl Res. 2011 Jun;157(6):326-31. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2011.01.006. Epub 2011 Feb 8. Transl Res. 2011. PMID: 21575916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IRF5 haplotypes demonstrate diverse serological associations which predict serum interferon alpha activity and explain the majority of the genetic association with systemic lupus erythematosus.Ann Rheum Dis. 2012 Mar;71(3):463-8. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200463. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012. PMID: 22088620 Free PMC article.
-
Autoimmune disease risk variant of IFIH1 is associated with increased sensitivity to IFN-α and serologic autoimmunity in lupus patients.J Immunol. 2011 Aug 1;187(3):1298-303. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100857. Epub 2011 Jun 24. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21705624 Free PMC article.
-
Association of IRF5 polymorphisms with increased risk for systemic lupus erythematosus in population of Crete, a southern-eastern European Greek island.Gene. 2017 Apr 30;610:9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.02.003. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28185859
-
Coordination between innate immune cells, type I IFNs and IRF5 drives SLE pathogenesis.Cytokine. 2020 Aug;132:154731. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.05.018. Epub 2019 May 23. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 31130331 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of NF-κB and PLCL2 as new susceptibility genes and highlights on a potential role of IRF8 through interferon signature modulation in systemic sclerosis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Mar 21;17(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0572-y. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25880423 Free PMC article.
-
Lupus enhancer risk variant causes dysregulation of IRF8 through cooperative lncRNA and DNA methylation machinery.Nat Commun. 2022 Apr 6;13(1):1855. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29514-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35388006 Free PMC article.
-
Causal variants in autoimmune disease: a commentary on a recent published fine-mapping algorithm analysis in genome-wide association studies study.Ann Transl Med. 2017 Mar;5(6):151. doi: 10.21037/atm.2017.02.26. Ann Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28462231 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Regional European genetic ancestry predicts type I interferon level and risk of severe viral infection.QJM. 2024 Aug 1;117(8):581-588. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcae052. QJM. 2024. PMID: 38530799
-
Type I Interferons in Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: Pathogenesis, Clinical Features and Treatment Options.Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2024 Jun 30;35(Suppl 2):365-380. doi: 10.31138/mjr.270324.tis. eCollection 2024 Jun. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39193187 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harley JB, Kelly JA, Kaufman KM. Unraveling the genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2006;28(2):119–30. - PubMed
-
- Graham RR, Kozyrev SV, Baechler EC, Reddy MV, Plenge RM, Bauer JW, et al. A common haplotype of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) regulates splicing and expression and is associated with increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet. 2006;38(5):550–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

